合金钢的机械加工和应力消除MACHINING OF ALLOY STEEL AND STRESS RELIEVING STEEL
1. INTRODUCTION 介绍
A.The data in this subject comes from Boeing Process Specifications BAC5436, BAC5440, BAC5617 and BAC5619. Access to the Boeing Process Specifications is available.
本主题中的数据来自波音工艺规范BAC5436、BAC5440、BAC5617和BAC5619。可访问波音工艺规范。
B.These procedures are recommended to help prevent problems which could decrease the service life of the component.
建议采用这些程序,以防止出现可能缩短部件使用寿命的问题。
C.Refer to SOPM 20-00-00 for a list of all the vendor names and addresses.
有关所有供应商名称和地址的列表,请参阅SOPM 20-00-00。
2. DEFINITIONS定义
A.Alloy steel — Steel that contains manganese, silicon or copper in quantities larger than those specified for carbon steels or they have specified ranges for one or more other alloying elements. The alloying additions improve mechanical properties, fabrication characteristics or other properties of the steel. Examples of high strength alloy steel include 4340M, 300M and others listed in section 4.B.
合金钢——含有锰、硅或铜的含量大于碳钢的规定,或者它们在规定范围内具有一种或多种其他合金元素的钢。合金添加剂改善了钢的机械性能、制造特性或其他性能。高强度合金钢的例子包括4340M、300M和第4.B节中列出的其他钢。
B.Corrosion resistant (CRES), precipitation hardened (PH) steel — Steel that contains significant quantities of chromium and nickel as alloying elements to promote corrosion resistance. Although highly alloyed, CRES alloys are not considered in the classification of “alloy steels”. Examples of CRES steels include 15-5PH, 17-4PH, 17-7PH, Custom 455 and Custom 465. Corrosion resistant steels are sometimes referred to as Stainless Steels.
耐腐蚀(CRES),沉淀硬化(PH)钢——含有大量铬和镍作为合金元素以提高耐腐蚀性的钢。尽管CRES是高合金,但并不认为在“合金钢”的分类中。CRES钢的例子包括15-5PH、17-4PH、17-7PH、Custom 455和Custom 465。耐腐蚀钢有时被称为不锈钢。
C.High strength steel — Generally, steel which is or can be heat treated to a strength level of 180 ksi or higher. For example, 4340 steel can be heat treated to levels between 125 and 220 ksi as specified in BAC5617, but it is given the name high strength steel because it can be heat treated to a strength level of 180 ksi or higher. Ultra high strength steels are capable of achieving strengths of more than 200 ksi.
高强度钢——一般来说,经过或可以经过热处理达到180 ksi或更高强度的钢。例如,4340钢可以热处理至BAC5617中规定的125-220 ksi,但它被命名为高强度钢,因为它可以热处理到180 ksi或更高。超高强度钢能够达到200 ksi以上的强度。
D.Intermediate alloy steel — Steel that has a higher alloy content than low alloy steels, but a lower alloy content than the stainless steels. Alloy 9Ni-4Co – 0.30C is considered an intermediate alloy steel.
中合金钢——合金含量比低合金钢高,但合金含量比不锈钢低的钢。合金9Ni-4Co-0.30C被认为是一种中合金钢。
E.KSI, ksi — An abbreviation for kips (1000 pounds) in a square inch. This is the standard unit of measure for strength of most metallic materials. The ksi value is used to measure or control the heat treat process, because metals are heat treated usually to increase their strength. Refer to BAC5617 for heat treatment details.
KSI,ksi——千磅/平方英寸的缩写。这是衡量大多数金属材料强度的标准单位。ksi值用于测量或控制热处理过程,因为金属通常经过热处理以提高其强度。有关热处理的详细信息,请参阅BAC5617。
F.Low alloy steel — Steel that is generally considered to contain a maximum of 5% alloying elements. In addition to carbon (up to about 1%), it has alloying elements such as manganese, silicon, nickel, chromium, molybdenum, vanadium and boron. The 4000-series steels are low alloy steels.
低合金钢——通常认为含有最多5%合金元素的钢。除了碳(高达约1%),它还含有合金元素,如锰、硅、镍、铬、钼、钒和硼。4000系列钢是低合金钢。
G.Steel — Ferrous alloys that contain up to 2% carbon.
钢——含碳量不超过2%的铁合金。
3. MATERIALS材料
NOTE: Equivalent substitutes can be used.
注:可以使用等效的替代品。
A.Alcohol — Denatured ethyl or methyl, technical grade, MIL-STD-1201 (SOPM 20-60-01)
酒精——变性乙基或甲基,技术等级,MIL-STD-1201(SOPM 20-60-01)
B.Alkaline cleaner — Clepo 26E, V92269
碱性清洁剂——Clepo 26E,V92269
C.Ammonium Persulfate — commercial grade
过硫酸铵——商业等级
D.Anti-smut additive — JAR-3N, Devonshire Consulting and Marketing Ltd., or V3WZG6
抗突变添加剂——JAR-3N,Devonshire Consulting and Marketing Ltd., or V3WZG6
E.Corrosion Preventive Compound — MIL-C-11796, Class 3 (SOPM 20-60-02).
防腐化合物——MIL-C-11796,3级(SOPM 20:60-02)
F.Cutting fluid (mineral oil) — Refer to BAC5008.
切削液(矿物油)——参考BAC5008。
G.Cutting fluid (water soluble) — Any water soluble cutting fluid can be used if it causes no corrosion on the part during the time it stays on the part
切削液(水溶性)——任何水溶性切削液都可以使用,只要它不会对零件造成腐蚀。
H.Hydrochloric Acid – 20-degree Baumé, technical grade, O-H-765
盐酸-20度Baumé,工业级,O-H-765
I.Hydrofluoric Acid – 48% reagent grade
氢氟酸-48%试剂级
J.Hydraulic Fluid – MIL-PRF-6083 (SOPM 20-60-03)
液压油-MIL-PRF-6083(SOPM 20-60-03)
K.Lubricating Oil – MIL-PRF-7870 (SOPM 20-60-03)
润滑油-MIL-PRF-7870(SOPM 20-60-03)
L.Lubricating Oil – MIL-PRF-21260 (SOPM 20-60-03)
润滑油-MIL-PRF-21260(SOPM 20-60-03)
M.Nitric Acid – 40-42-degree Baumé, technical grade, O-N-350
硝酸-40-42度Baumé,工业级,O-N-350
N.Sodium hydroxide – Flake or granulated, technical grade, O-S-598
氢氧化钠-片状或颗粒状,工业级,O-S-598
O.Solvent – P-D-680, Type 1 or aliphatic naphtha TT-N-95, Type 2 (SOPM 20-60-01)
溶剂-P-D-680,1型或aliphatic naphtha TT-N-95,2型(SOPM 20-60-01)
P.Temporary protective coatings as specified in BAC5034 (SOPM 20-44-02), Type 3, Class 2
BAC5034(SOPM 20-44-02)中规定的临时保护涂层,类型3,等级2
4. GENERAL概述
A.This subject tells how to machine high strength steels that are listed in Figure 1 when they are in the fully hardened condition. These steels include, but are not limited to, high strength low and intermediate alloy steels, ultra high strength steels, and CRES PH steels. Also described is how to stress relieve steels (see the section on Post Machining Treatments and Figure 1).To remove metal from steels before they are hardened, tempered or heat-treated, use standard industry practices. Refer to SOPM 20-10-01 for repair and refinish of high strength alloy steels.
本主题告诉如何加工图1中列出的处于完全硬化状态的高强度钢。这些钢包括但不限于高强度低和中合金钢、超高强度钢和CRES PH钢。还介绍了如何消除钢的应力(参见“机加工后处理”章节和图1)。要在钢材硬化、回火或热处理之前去除钢中的金属,请使用标准工业程序。关于高强度合金钢的修理和表面处理,请参阅SOPM 20-10-01。
B.Some of the procedures in this subject refer to alloy steels by types. These types are identified below. This comes from BAC5440 Table I.
本主题中的一些程序按类型涉及合金钢。这些类型如下所示。这来自BAC5440表I。
(1)Type 1: 4130, 4140, 4330M, 4340, and D6AC steels, all 180-200 ksi
类型1:4130、4140、4330M、4340和D6AC钢,都为180-200 ksi
(2)Type 2: 4330M steel, 220-240 ksi
类型2:4330M钢,220-240 ksi
(3)Type 3: 4340 steel, 260-280 ksi
类型3:4340钢,260-280 ksi ksi
(4)Type 4: 300M steel, 4340M steel, and Aermet 100 (UNS K92580) steel, all 270 to 300 ksi
类型4:300M钢、4340M钢和Aermet 100(UNS K92580)钢,都为270-300 ksi
(5)FL 1: 52100 steel, Rockwell C hardness 55-65 (recommended that grinding be the only metal removal operation at this hardness level)
FL 1:52100钢,洛氏硬度55-65(建议在该硬度水平下,磨削是唯一的金属去除操作)
(6)Type 5: 9Ni – 4Co – 0.20C (BMS 7-182, Type 4) steel, 190-210 ksi
类型5:9Ni-4Co-0.20C(BMS 7-182,4型)钢,190-210 ksi
(7)Type 6: 9Ni – 4Co – 0.30C (BMS 7-182, Type 2) steel, 220 ksi minimum
类型6:9Ni-4Co-0.30C(BMS 7-182,2型)钢,最小220 ksi
C.Use a cutting fluid unless the detailed instructions are different. Make sure the fluid is continuously supplied to the tool edge as it cuts. Do not use cutting fluids that contain free sulfur or chlorine unless the parts can be disassembled and cleaned.
除非有不同的详细说明,否则请使用切削液。确保在切割时持续向刀具边缘供应液体。除非零件可以分解和清洁,否则不要使用含有游离硫或氯的切削液。
D.Use power screw feed equipment or other power equipment that gives a controlled positive feed unless for operations that chamfer, make radii, hone, remove burrs, or hand ream.
除非是倒角、制造半径、珩磨、去除毛刺或手动铰削的操作,则使用动力螺旋进给设备或其他可提供受控正进给的动力设备。
E.Cleaning and Storing of Parts
零件的清洁和储存
(1)When you use cutting fluids that contain free sulfur or chlorine, clean the part to remove all fluid when you remove the part from the machine at the end of an operation.
当您使用含有游离硫或氯的切削液时,在操作结束时从机器上取下零件时,应清洁零件以清除所有液体。
(2)If you remove the part only for a change of position, wipe off or drain the fluid from the part before you continue the operation.
如果拆卸零件只是为了改变位置,请在继续操作之前擦掉或排出零件中的液体。
(3)If you do not work on the part (in or out of the machine) for more than 2 hours, wipe off all unwanted fluid from the part and cover it with MIL-PRF-7870 oil.
如果您超过2小时不加工零件(在机器内或机器外),请擦掉零件上所有不需要的液体,并用MIL-PRF-7870油覆盖。
(4)Within 1 hour after you remove the part from the machine for last time, put the part in solvent to clean off the cutting fluid. If applicable, clean the part again as required by other overhaul instructions such as application of sealant or protective finishes.
最后一次从机器上取下零件后1小时内,将零件放入溶剂中以清除切削液。如果适用,按照其他大修说明的要求,再次清洁零件,如涂抹密封剂或保护性面漆。
5. SURFACE GRINDING表面研磨
CAUTION:IF THE SURFACE IS CHROME PLATED, GRIND IT PER SOPM 20-10-04.
注意:如果表面是镀铬的,请按照SOPM 20-10-04进行研磨。
NOTE: These procedures are for open surfaces and holes larger than 2.500 inches in diameter. For smaller holes, refer to the Hole Grinding procedure in Paragraph 9.D.
注:这些程序适用于直径大于2.500英寸的开口表面和孔。对于较小的孔,请参考第9.D段中的孔研磨程序。
A.Use these procedures to grind surfaces, cylindrical or flat, of steels of all alloys in all heat-treat ranges and carburized parts. You can use other procedures if the results will agree with the inspection requirements. Make sure the surface has no unwanted material on it before you grind.
使用这些程序研磨所有热处理范围内的所有合金钢和渗碳零件的圆柱形表面或平面。如果结果符合检验要求,您可以使用其他程序。在研磨之前,确保表面没有多余的材料。
B.During the grind, give the surface a good flow of filtered, water-soluble coolant. Adjust the nozzle to give a continuous flow of the coolant across the full width of the wheel.
在研磨过程中,给表面提供良好的过滤水溶性冷却液。调整喷嘴,使冷却液在车轮的整个宽度上连续流动。
C.Dress the grinding wheel frequently to keep it sharp and clean. Turn the diamond dressing tool frequently to keep its edge sharp. Move the diamond across the wheel at 10-20 inches per minute.
经常修整砂轮,使其保持锋利和清洁。经常转动金刚石修整工具,使其边缘锋利。以每分钟10-20英寸的速度在轮子上移动金刚磨石。
D.To make sure the surfaces do not become too hot, use the recommended values given in Table 1.
为了确保表面不会变得太热,请使用表1中给出的推荐值。
|
Table 1: Surface Grinding Controls表面研磨控制 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
6. TURNING AND SHAPING车削和成形
A.The values given in Table 2 are recommended for all turning and shaping operations which will subsequently be treated as specified in Paragraph 10. This includes internal surfaces larger than 2.50 inch diameter which are bored on lathe-type equipment or boring-mill machines. Equivalent procedures can be used if they give results of the same quality.
建议使用表2中给出的值来用于所有车削和成形操作,这些操作随后将按照第10段的规定进行处理。这包括在车床设备或镗床上钻的孔的直径大于2.50英寸的内表面。可以使用得到相同质量的结果等效程序。
B.Use a good flow of cutting fluid.
使用良好流量的切削液。
|
Table 2: Turning and Shaping Controls车削和成形控制 |
|||||||||||||||
|
7. MILLING铣削
A.Use these procedures to mill heat-treated steels Types 1 thru 6. You can use other procedures if the results will agree with the inspection requirements.
使用这些程序来铣削1-6型热处理钢。如果结果符合检验要求,您可以使用其他程序。
B.Set up the part and the tool to be as rigid as possible. Use the shortest possible cutter length.
将零件和工具设置为尽可能坚硬。使用尽可能短的刀具长度。
C.During the procedure, examine the tool and the part frequently for tool wear or damage, or changes to the surface finish of the milled surface. Sharpen or replace the tool as necessary. Use a good flow of cutting fluid.
在该过程中,经常检查工具和零件是否有工具磨损或损坏,或铣削表面的表面光洁度是否发生变化。必要时打磨(锐化)或更换工具。使用良好流量的切削液。
D.Refer to Table 3, Table 4, or Table 5, as applicable, for recommended values for end milling, face milling, and side or slot milling.
参考表3、表4或表5(如适用),了解末端铣削、端面铣削和侧面或槽铣削的推荐值。



8. BREAKING EDGES AND BLENDING 倒角和混合
A.All procedures that remove burrs, make chamfers or radii, smooth mismatches, or do equivalent operations must let the surfaces agree with the overhaul instructions.
所有去除毛刺、加工倒角或半径、光顺配合面或进行等效操作的程序都必须使表面符合大修说明。
B.Any hand tool without power, such as a file or emery paper, can be used to make radii or break edges. Hand-held power tools can be used to remove burrs or make radii. Rotary burrs and files in portable hand-held motors can be used if the speed is kept to a limit of 500 rpm maximum.
任何没有动力的手动工具,如锉刀或金刚砂纸,都可以用来制作半径或倒角。手持式电动工具可用于去除毛刺或制作半径。如果速度保持在最大500转/分的限制内,则可以使用便携式手持电机旋转去除毛刺和锉刀。
C.Abrasive tools with paper or cloth backs, such as cones, discs, drums, rotary wheels or wrapped products, can be used in portable hand-held motors if this does not make a shower of sparks. Make sure you apply the tool with only light pressure and do not let the tool stay at one location on the surface of the part.
背面是纸或布的研磨工具,如锥形、圆盘、滚筒、转轮或包裹物,如果不会产生火花,可以用于便携式手持电机。确保仅用轻微的压力施加在工具上,不要让工具停留在零件表面的一个位置。
9. HOLE PREPARATION钻孔准备
A.Drilling
钻孔
(1)On holes 1/4 inch diameter or larger, use a center drill as a pilot if you do not use a drill fixture or bushing.
在直径1/4英寸或更大的孔上,如果不使用钻孔夹具或衬套,则使用中心钻作为导向器。
(2)Sharpen or replace drill bits at the first sign they start to cut incorrectly, they chatter, or if there is an increase in noise level or a change in hole finish.
一旦出现钻头开始切割不正确、发出刺耳声音或噪音增加或孔光洁度发生变化的迹象,就应打磨或更换钻头。
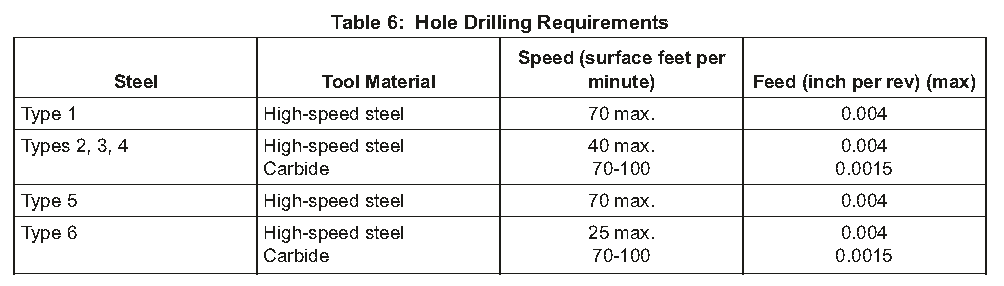
(3)Drill bits with positive rake angles must be used. Use a good flow of cutting fluid. For other requirements, see Table 6.
必须使用具有正倾角的钻头。使用良好流量的切削液。其他要求见表6。
B.Hole Reaming
扩孔
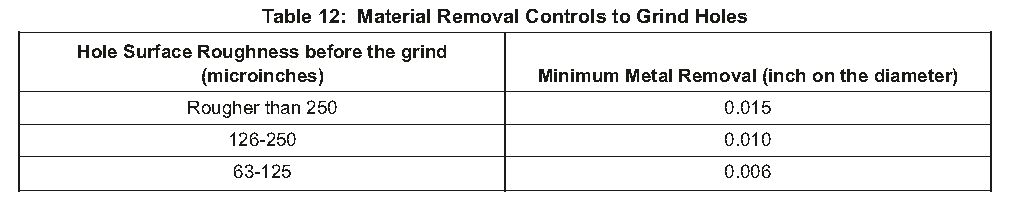
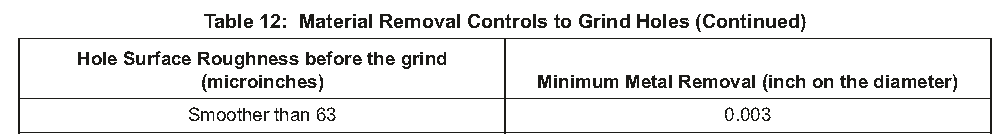
(1)Holes to be reamed to the completed diameter must remove a specified thickness of metal. This metal can be removed by a one-ream operation or a two-ream operation as specified in Table 7.
要扩至完整直径的孔必须去除指定厚度的金属。这种金属可以通过表7中规定的一令操作或两令操作去除。
(2)Holes to be completed by a combination of ream and hone or grind operations must make the ream operation remove a minimum of 1/32 inch from the diameter. For steels 260-300 ksi, two removals of 1/64 inch from the diameter can be used as an alternative to one 1/32-inch removal.
通过扩孔和珩磨或研磨操作组合完成的孔必须使用扩孔操作将直径至少减少1/32英寸。对于260-300 ksi的钢,可以使用从直径上去除两次1/64英寸来代替一次1/32英寸。
(3)See Table 7 for the metal removal and number of ream operations necessary. Make selections of feed, speed, tool, and cutting fluid from Table 8. See Table 9 for maximum tool life limits, but sharpen or replace reamers at the first sign of wear or damage that could change the surface finish of the hole.
金属去除和必要的扩孔操作次数见表7。从表8中选择进给、速度、工具和切削液。关于刀具的最大使用寿命限制,请参见表9,但在出现磨损或损坏的首个迹象(可能会改变孔的表面光洁度)时,应打磨或更换铰刀。
(4)Use a good flow of cutting fluid when you ream holes with power equipment.
使用动力设备扩孔时,请使用良好流量的切削液。
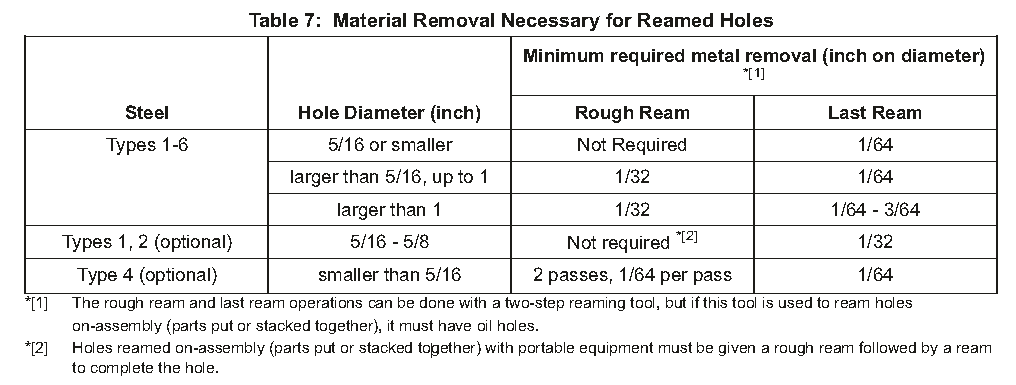
*[1] The rough ream and last ream operations can be done with a two-step reaming tool, but if this tool is used to ream holes on-assembly (parts put or stacked together), it must have oil holes.
*[1] 粗铰和最后铰操作可以使用两步铰孔工具进行,但如果该工具用于在组件上铰孔(将零件放在一起或堆叠在一起),则必须有油孔
*[2] Holes reamed on-assembly (parts put or stacked together) with portable equipment must be given a rough ream followed by a ream to complete the hole.
*[2] 使用便携式设备在组件(将零件放在一起或堆叠在一起)上铰孔时,必须先进行粗铰,然后再进行铰孔,以完成钻孔。
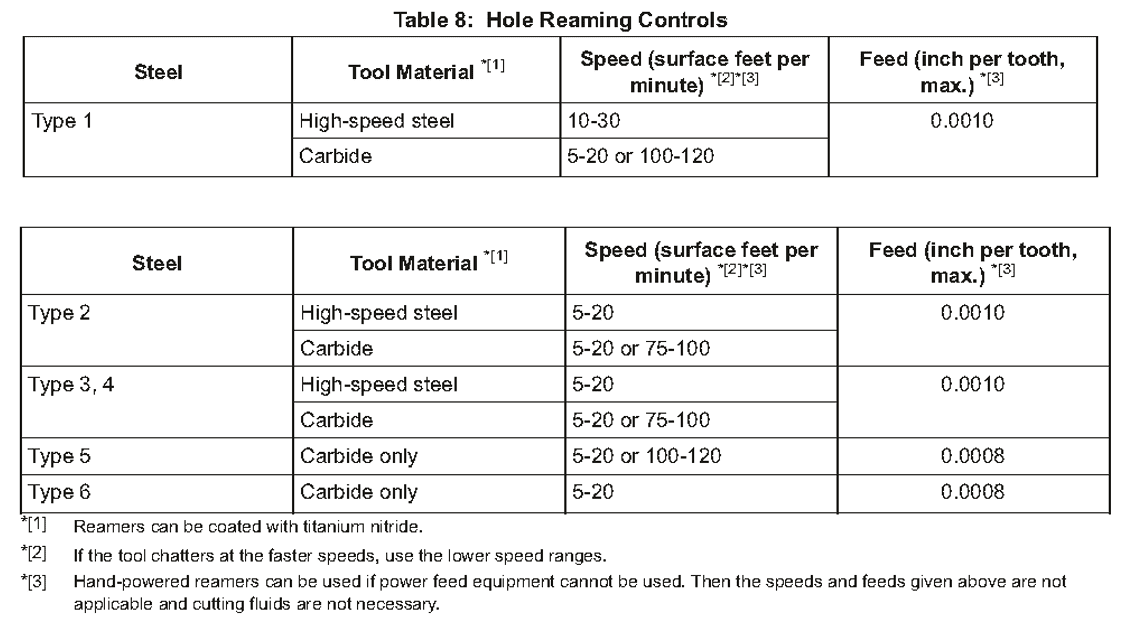
*[1] Reamers can be coated with titanium nitride.
*[1] 铰刀可以涂氮化钛
*[2] If the tool chatters at the faster speeds, use the lower speed ranges.
*[2] 如果工具在较快的速度下抖动,则使用较低的速度范围
*[3] Hand-powered reamers can be used if power feed equipment cannot be used. Then the speeds and feeds given above are not applicable and cutting fluids are not necessary.
*[3] 如果不能使用动力进给设备,可以使用手动铰刀。则上述速度和进给量不适用,也不需要切削液。

*[1] Maximum number of last-ream operations permitted for each reamer before it must be sharpened or replaced.
*[1] 每个铰刀在必须磨尖或更换之前允许的最后一次扩孔操作的最大次数。
C.Hole Boring
钻孔
(1)This procedure is for all bored holes 2.500 inches in diameter or smaller. For larger holes, use the turning procedure of Paragraph 6..
此程序适用于直径小于等于2.500英寸的所有钻孔。对于较大的孔,使用第6段的车削程序。
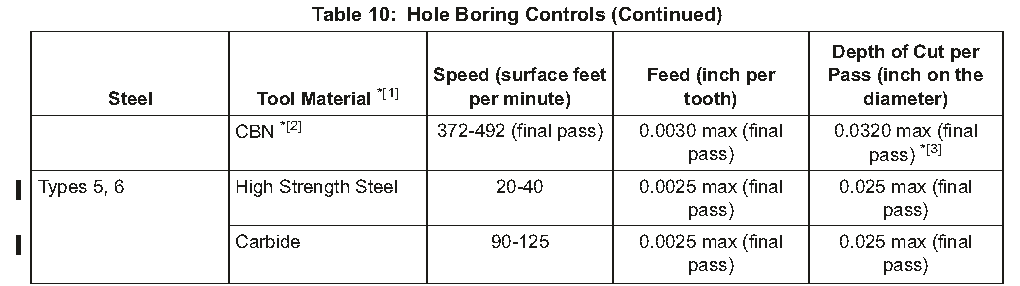
(2)Holes to be bored to their final diameter must have a minimum of 3/64 inch metal removal on the diameter. For these holes, use the controls of Table 10
待钻至其最终直径的孔在直径尺寸上必须至少有3/64英寸的金属去除量。对于这些孔,使用表10中数据来控制。
(3)Some holes are bored first, and then reamed, honed, or ground to final size. When you bore these holes, remove a minimum of 1/32 inch on the diameter. If you then ream the holes, remove a minimum of 1/64 inch on the diameter. If you hone or grind the hole, the depth is controlled by surface roughness.
一些孔首先钻孔,然后扩孔、珩磨或研磨至最终尺寸。当钻这些孔时,至少要去除直径上的1/32英寸。如果随后进行扩孔,则在直径上至少去除1/64英寸。如果你珩磨或研磨,深度是由表面粗糙度控制的。
(4)Replace or sharpen the tool at the first sign that the tool does not cut correctly.
在出现刀具切割不正确的首个迹象时,更换或打磨刀具。
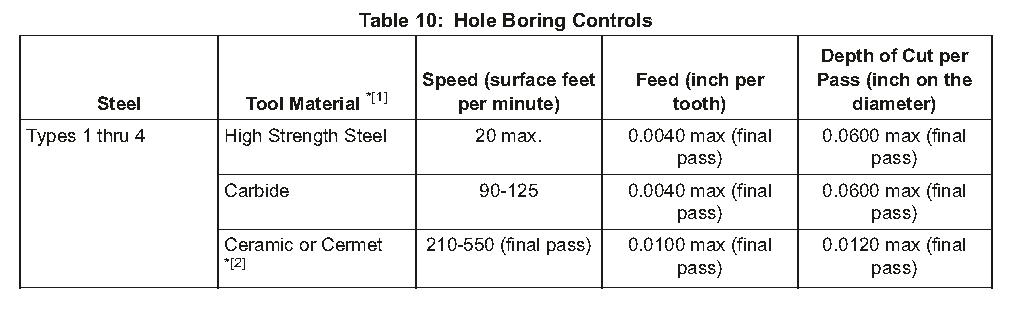
*[1] High-speed steel or carbide tools can be coated with titanium nitride or layers of hard coatings (titanium carbide, aluminum oxide, titanium nitride) but the outer layer must be titanium nitride.
*[1] 高速钢或硬质合金工具可以涂有氮化钛或硬质涂层(碳化钛、氧化铝、氮化钛),但外层必须是氮化钛
*[2] Cutting fluid is optional when you bore with ceramic, cermet or CBN tools.
*[2] 当您使用陶瓷、金属陶瓷或CBN工具钻孔时,切削液是可选的
*[3] Minimum depth of the cut (inch on the diameter) per pass must be a minimum of 2 times the CBN tool edge preparation.
*[3] 每次焊道的最小切割深度(直径上的英寸)必须至少是CBN工具边缘预设的2倍。
D.Hole Grinding
磨孔
(1)This procedure is for all ground holes 2.500 inches in diameter or smaller. For larger holes, use the surface grinding procedure of Paragraph 5.
此程序适用于直径≤2.500英寸的所有接地孔。对于较大的孔,使用第5段中的表面研磨程序。
(2)Other procedures are preferred to complete a hole. The grind procedure is optional when the other procedures cannot give the specified surface finish and diameter tolerance.
最好采用其他程序来完成钻孔。当其他程序不能提供指定的表面光洁度和直径公差时,可选研磨程序。
(3)To use this procedure to complete a hole:
使用此程序来完成孔:
a)Drill the hole as specified in Paragraph 9.A.
按照第9.a.段的规定钻孔。
b)Ream the hole as specified in Paragraph 9.B. or bore the hole as specified in Paragraph 9.C. Remove 1/32-inch material on the diameter.
按照第9.b.段的规定铰孔或按照第9.C段的规定镗孔。去除直径上的1/32英寸材料。
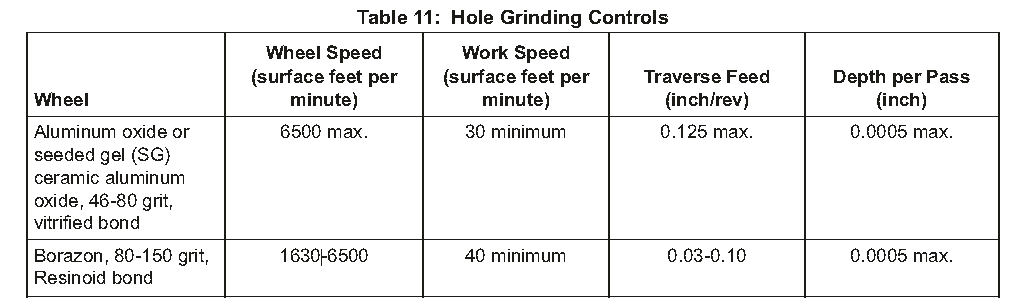
c)Grind the hole to the specified dimensions. Use the controls of Table 11.
将孔打磨至规定尺寸。按表11控制。
d)Continuously flush internal diameters with cutting fluid.
用切削液连续冲洗内径。
E.Hole Honing
珩磨
(1)For holes to be drilled, then reamed or bored, and then honed:
对于要钻孔,然后铰孔或钻孔,然后珩磨的孔:
a)Drill the hole as specified in Paragraph 9.A.
按照第9.a.段的规定钻孔。
b)Ream to remove 1/32 inch on the diameter, but for holes 5/16-inch or smaller, you must remove only 1/64 inch on the diameter. Or bore the hole to remove 1/32 inch on the diameter.
铰孔以去除直径上的1/32英寸,但对于5/16英寸或更小的孔,必须仅去除直径的1/64英寸。或者钻孔以去除直径上的1/32英寸。
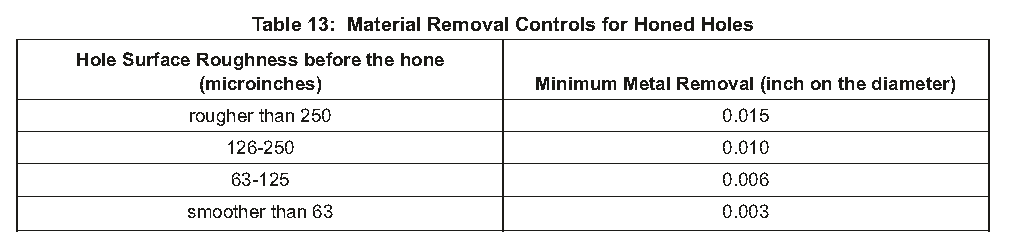
c)For 5/16 inch diameter reamed holes, hone as specified in Table 13 to the specified dimensions.
对于5/16英寸直径的铰孔,按照表13的规定将其珩磨至规定尺寸。
F.Broaching — Do not broach holes in steels that are more than 200 ksi. Broach holes in steels heat-treated to 180-200 ksi only when permitted by the overhaul instructions.
拉通孔——不要在大于200 ksi的钢材上拉通孔。只有在大修说明允许的情况下,才能在热处理至180-200 ksi的钢材上进行拉通孔。
G.Other Hole Preparation Techniques — Do not use other procedures unless the overhaul instructions are different or the procedure is approved. Refer to BAC5440 for details.
其他钻孔准备技术——除非大修说明不同或程序获得批准,否则不要使用其他程序。详见BAC5440。
H.Chamfering, Radiusing, and Removal of Burrs
倒角、半径和毛刺去除
(1)All procedures that remove burrs or make chamfers or radii must let the surfaces agree with the overhaul instructions.
所有去除毛刺或加工倒角或半径的程序都必须使表面符合大修说明。
(2)When you use a machine to make the chamfer or countersink, you must remove 0.010 inch or more material. The machine can be hand-feed or positive-feed. With hand-feed equipment, make the chamfer in two cuts: a rough cut to within 0.005-0.010 inch of the finish (design) dimensions, and then a last cut. With positive-feed equipment with a maximum feed of 0.004 inch per revolution, you can make the chamfer in one cut. The tool speed must be 100 rpm maximum for the two types of feed. After each cut, examine the hole for defects caused by bad or worn cutters. Replace cutters as necessary.
使用机器进行倒角或锪孔时,必须去除0.010英寸或更多的材料。该机器可以是手动进给或正进给。使用手动进给设备,分两次切割倒角:一次粗切割至表面(设计)尺寸的0.005-0.010英寸以内,然后进行最后一次切割。使用每转最大进给量为0.004英寸的正进给设备,您可以一次加工出倒角。对于两种类型的进给,刀具速度必须最大为100 rpm(转/分钟)。每次切割后,检查孔是否存在由坏的或磨损的刀具引起的缺陷。按需更换刀具。
(3)Any hand tool without power, such as a file or emery paper, can be used to make radii or break the edges of the holes. Hand-held power tools can be used to remove burrs or make radii on holes. Rotary burrs and files in portable hand-held motors can be used if you keep the speed to 500 rpm maximum.
任何没有动力的手动工具,如锉刀或金刚砂纸,都可以用来倒圆或折断孔的边缘。手持电动工具可用于去除毛刺或在孔上倒圆。如果将转速保持在最大500转/分,则可以使用便携式手持电动工具来旋转磨石和锉刀。
(4)Abrasive tools with paper or cloth backs, such as cones, discs, drums, rotary wheels or wrapped products, can be used in portable hand-held motors if this does not make a shower of sparks. Make sure you apply the tool with only light pressure and do not let the tool stay at one location on the surface of the part.
背面为纸或布研磨工具,如锥形、圆盘、滚筒、转轮或缠绕包裹物,如果不会产生火花,可以用于便携式手持电机。确保仅用轻微的压力施加工具,不要让工具停留在零件表面的一个位置。
(5)The surface of the hole and the chamfer must have no nicks, gouges, scratches, chatter marks, machine tears or cracks.
孔和倒角表面不得有刻痕、凿痕、划痕、颤振痕迹、机械撕裂或裂纹。
10. POST MACHINING TREATMENTS机加工后处理
A.On all steel parts with surface areas which were machined or ground in the hardened and tempered condition, do these steps:
在所有具有在淬火和回火条件下加工或研磨的表面区域的钢零件上,执行以下步骤:
(1)Visually examine the surface for discoloration from overheating
目视检查表面是否因过热而变色
(2)Surface temper etch examine the alloy steels that are 180 ksi or above, but not the corrosion resistant steels, as specified in Paragraph 11.
表面回火蚀刻检查180 ksi或以上的合金钢,但不检查第11段中规定的耐腐蚀钢。
NOTE: The visual and etch examinations are not necessary for holes smaller than 1.0 inch diameter, or for holes 1.0-2.5 inch diameter that have a depth-to-diameter ratio of 1.5 or more. If the hole is open at each end, the depth is measured to the center of the bore.
注:对于直径小于1.0英寸的孔,或深度与直径之比为1.5或更大的直径为1.0-2.5英寸的孔不需要进行目视检查和蚀刻检查。如果孔的每一端都是开口的,则测量孔中心的深度。
(3)Stress relieve.
消除应力。
NOTE: If during overhaul of a hardened steel part, the only operation is the repair of holes smaller than 2.5 inches in diameter and all hole preparation parameters as specified in SOPM 20-10-02 are obeyed during this repair, it is not necessary to stress relieve the part.
注:如果在淬火钢零件的大修过程中,唯一的操作是修理直径小于2.5英寸的孔,并且在修理时依据SOPM 20-10-02中规定的孔的准备参数,则无需对零件进行应力释放。
NOTE: In case of a conflict between the instructions of this SOPM 20-10-02 and the CMM, specifications, or SOPM’s used during overhaul, the CMM, specification, or SOPM instructions take precedence.
注:如果SOPM 20-10-02的说明与大修期间使用的CMM、规范或SOPM之间存在冲突,则以CMM、规范和SOPM的说明为准。
NOTE: Make sure to check the CMM and referenced SOPM’s for instructions about when to stress relieve when removing finishes, cleaning, passivating, grinding or before plating (including High Strength CRES alloys).
Typically stress relief is not necessary for corrosion resistant steels A-286 and 300 series, 17-7PH (CH900), nickel alloys 625 and 718, and copper alloys.
Typically stress relief is not necessary for non-threaded corrosion resistant precipitation hardened steels PH13-8Mo, 15-5PH, 17-4PH and 17-7PH, at strength levels less than 180 ksi that will not be plated (or for threaded parts below 160 ksi).
注:在去除表面处理、清洁、钝化、研磨或电镀(包括高强度CRES合金)之前,请务必检查CMM和参考的SOPM,以获取有关何时应力消除的说明。
通常,抗腐蚀钢A-286和300系列、17-7PH(CH900)、镍合金625和718以及铜合金不需要消除应力。
通常,对于强度水平小于180 ksi的非螺纹耐腐蚀沉淀硬化钢PH13-8Mo、15-5PH、17-4PH和17-7PH,不需要消除应力(或对于强度低于160 ksi的螺纹零件)。
NOTE: Stress relief could be necessary in some procedures, such as cleaning as specified in BAC5625, stripping as specified in BAC5771, after removal of coatings or plating by grinding as specified in BAC5855 or BAC5032, before plating operations, for threaded CRES alloys heat treated to 160 ksi and above or for non-threaded CRES alloys heat treated to 180 ksi and above.
注:在某些程序中可能需要消除应力,例如按照BAC5625的规定进行清洁,按照BAC5771的规定进行剥离,在按照BAC5855或BAC5032的规定通过研磨去除涂层或镀层之后,在镀层操作之前,对于热处理至160 ksi及以上的螺纹CRES合金或热处理至180 ksi及以下的非螺纹CRES合金而言。
a)Stress relief will decrease surface residual stresses that were caused during some metal removal practices. But hand tools without power, such as files or emery paper, do not cause sufficient residual stresses to make stress relief necessary.
应力消除将减少在某些金属去除过程中产生的表面残余应力。但是,没有动力的手动工具,如锉刀或金刚砂纸,不会产生足够的残余应力来消除应力。
b)Stress relieve as specified in Figure 1. As an option, stress relief at 350-400°F for 4 hours can be used as indicated in Figure 1, but will not give as much stress relief.
应力释放如图1所示。作为一种选择,如图1所示,可以在350-400°F下使用4小时的应力消除,但不会产生那么多的应力释放。
c)If you make a new part of high-strength alloy steel and the part will get a second heat treatment after it is heat treated and machined, that second temper can be used for this stress relief.
如果你用高强度合金钢制造一个新零件,并且该零件在经过热处理和机械加工后将进行第二次热处理,则第二次回火可用于消除应力。
d)For new parts hole drilling operations of less than 2.5 inches in diameter, no additional stress relief is required.
对于直径小于2.5英寸的新零件钻孔操作,不需要额外的应力消除。
e)If the alloy steel part was stress relieved, and then small areas were repaired with portable hand-held power tools as specified in Paragraph 8., a second stress relief is not necessary if you etch examine the part by the Nital etch procedure (preferred) or the ammonium persulfate etch procedure (optional) (Paragraph 11.).
如果对合金钢零件进行了应力消除,然后使用第8段中规定的便携式手持式电动工具对小面积区域进行了维修,则如果通过Nital蚀刻程序(首选)或过硫酸铵蚀刻程序(可选)对零件进行蚀刻检查,则无需进行第二次应力消除(第11段)。
f)Before plating, stress relief is not necessary for:
电镀前,以下情况无需消除应力:
1)Parts which were not ground, machined, straightened, cold worked or proof loaded after heat treatment.
热处理后未经研磨、机加工、矫直、冷加工或加压的零件。
2)Parts which were only honed, lapped, or repaired with unpowered hand tools after heat treatment.
热处理后仅使用无动力手动工具进行珩磨、研磨或修理的零件。
3)Parts which were stress relieved before they were shot peened or before some other plating. This includes plating which was stripped for plating replacement.
在喷丸处理或其他电镀之前应力消除的零件。这包括为更换镀层而剥离的镀层。
(4)Apply MIL-PRF-7870 oil unless the stress relief is followed by a magnetic particle check within 2 hours.
涂抹MIL-PRF-7870油,除非应力消除后在2小时内进行磁粉检查。
(5)Magnetic particle examine (SOPM 20-20-01).磁粉检测(SOPM 20-20-01)。
(6)Apply MIL-C-11796, Class 3 corrosion preventive compound, but use MIL-PRF-7870 oil if more work will be done on the part in the next 48 hours. Hot dip coatings can be used for dry storage of noncarburized parts up to 6 months. If a cut or break goes through the coating, immediately strip the part and apply the coating again.
使用MIL-C-11796,3级防腐化合物,但如果在接下来的48小时内需要对零件进行更多的工作,则使用MIL-PRF-7870油。热浸涂层可用于非渗碳零件的干储存长达6个月。如果涂层出现切口或断裂,应立即剥去零件并再次涂覆涂层。
(7)Do all finishing operations such as shot peening, honing, lapping, or plating required by overhaul instructions on machined surfaces after you do the procedures in Paragraph 10.A. On surfaces made by hand-held tools without power (such as a file or emery cloth used to make radii or break sharp edges), it is not necessary to do the surface temper etch examination, the stress relief, or the magnetic particle examination.
在完成第10.A段中的程序后,在机械加工表面上进行大修说明要求的所有精加工操作,如喷丸、珩磨、研磨或电镀。在由无动力手持工具(如用于倒圆或折断锐边的锉刀或砂布)制成的表面上,无需进行表面回火蚀刻检查、应力消除或磁粉检查。
(8)If more than 60 minutes occur between the etch or the inspection and the bake, or subsequent work, give the parts protection with MIL-PRF-21260 or other soft films, oils and greases as specified in BAC5034 (SOPM 20-44-02).
如果蚀刻/检查与烘烤/后续工作之间的时间超过60分钟,则使用MIL-PRF-21260或BAC5034(SOPM 20-44-02)中规定的其他软膜、油和油脂对零件进行保护。
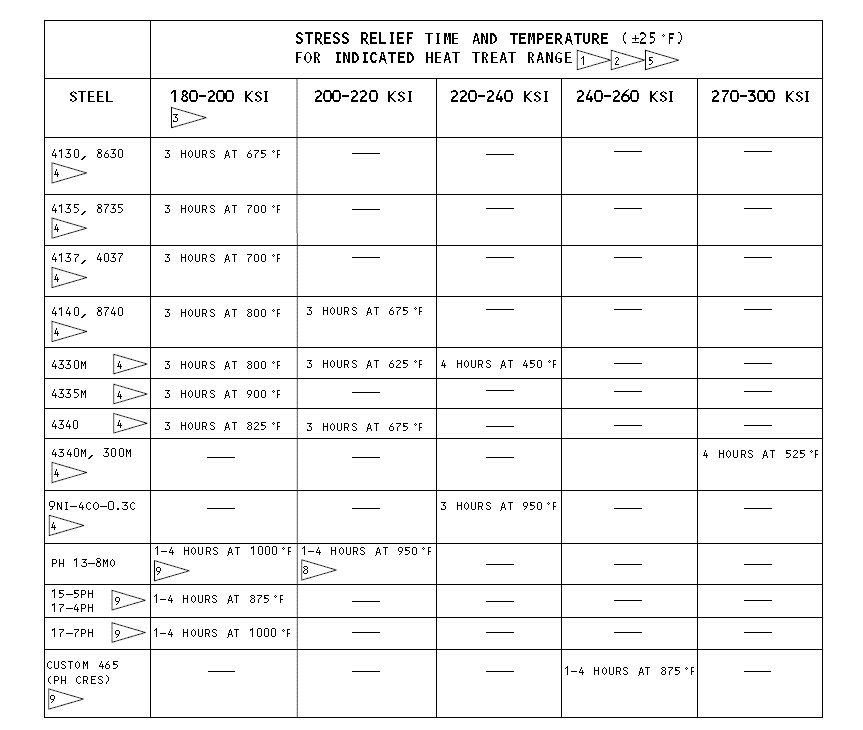
Stress Relief Table
Figure 1 (Sheet 1 of 3)
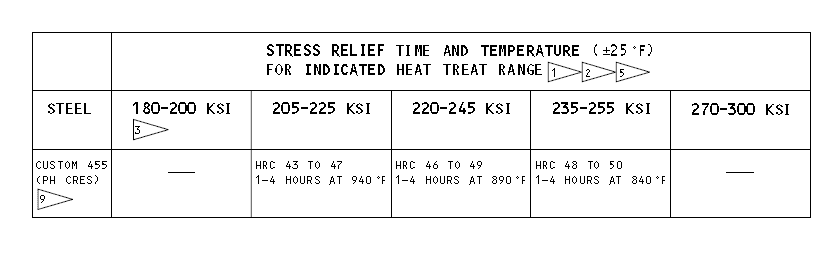
Stress Relief Table
Figure 1 (Sheet 2 of 3)
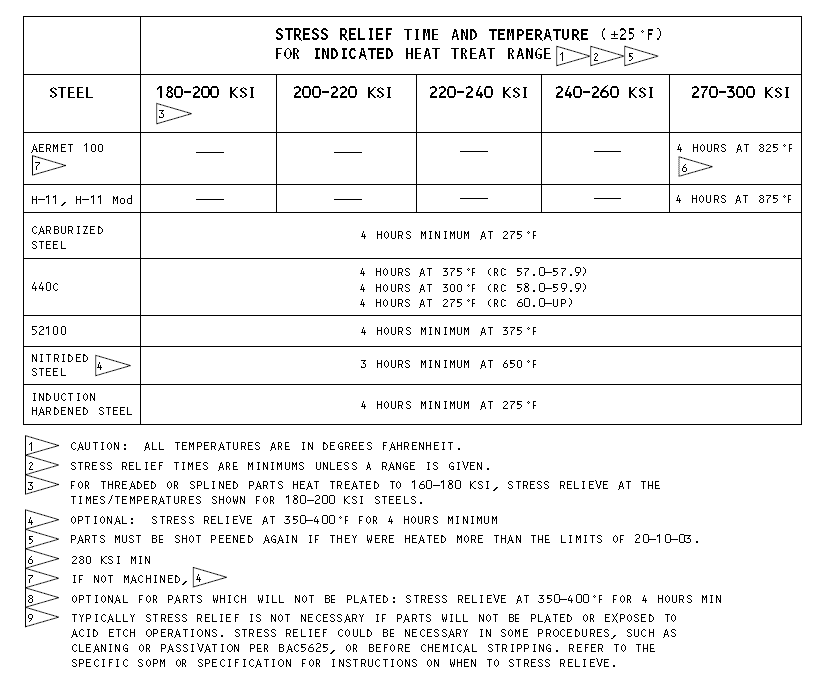
Stress Relief Table
Figure 1 (Sheet 3 of 3)
*[1] CAUTION: ALL TEMPERATURES ARE IN DEGREES FAHRENHEIT.
*[1]注意:所有温度都以华氏度为单位。
*[2]STRESS RELIEF TIMES ARE MINIMUMS UNLESS A RANGE IS GIVEN.
*[2]除非给出一个范围,否则应力消除时间是最小的。
*[3]FOR THREADED OR SPLINED PARTS HEAT TREATED TO 160-180 KSI, STRESS RELIEVE AT THE TIMES/TEMPERATURES SHOWN FOR 180-200 KSI STEELS.
*[3]对于热处理至160-180ksi的螺纹或花键零件,在180-200 KSI钢所示的时间/温度下消除应力。
*[4]OPTIONAL: STRESS RELIEVE AT 350-400 °F FOR 4 HOURS MINIMUM
*[4]可选:在350-400°F下至少4小时的应力消除
*[5]PARTS MUST BE SHOT PEENED AGAIN IF THEY WERE HEATED MORE THAN THE LIMITS OF 20-10-03.
*[5]如果零件的加热超过20-10-03的限制,则必须再次对其进行喷丸处理。
*[6]280 KSI MIN
*[6]最小280ksi
*[7]IF NOT MACHINED,
*[7]如果不进行机械加工,*[4]
*[8] OPTIONAL FOR PARTS WHICH WILL NOT BE PLATED: STRESS RELIEVE AT 350-400 °F FOR 4 HOURS MIN
*[8] 对于未电镀的零件,可选择:在350-400°F下至少4小时消除应力
*[9] TYPICALLY STRESS RELIEF IS NOT NECESSARY IF PARTS WILL NOT BE PLATED OR EXPOSED TO ACID ETCH OPERATIONS. STRESS RELIEF COULD BE NECESSARY IN SOME PROCEDURES, SUCH AS CLEANING OR PASSIVATION PER BAC5625, OR BEFORE CHEMICAL STRIPPING. REFER TO THE SPECIFIC SOPM OR SPECIFICATION FOR INSTRUCTIONS ON WHEN TO STRESS RELIEVE.
*[9] 如果零件将不被电镀或暴露于酸蚀刻工作中,则通常不需要应力消除。在某些程序中,如根据BAC5625进行清洁或钝化,或在化学剥离之前,可能需要消除应力。有关何时应力消除的说明,请参阅特定的SOPM或规范。
11. EXAMINATION FOR HEAT DAMAGE热损伤检查
A.General
通用
(1)Incorrect material removal procedures will make the part too hot and will cause heat damage. The etch inspection procedure will help you find retempering burns, rehardening burns, grinding or machining burns, and other heat-related damage.
不正确的材料去除程序会使零件过热,并导致热损坏。蚀刻检查程序将帮助您发现再回火烧伤、再硬化烧伤、研磨或机加工烧伤以及其他与热相关的损伤。
(2)Visually examine all completed holes and completed machined surfaces for the specified surface roughness and to see if they became too hot. The surface quality (such as local differences from the specified contour, nicks, gouges, and scratches) must agree with standard industry practices. Parts are unserviceable if they have color changes (such as a blue or dark gray tint) because they became too hot, or if they have tears, chatter marks, or cracks. The surface roughness of holes must be 125 microinches or smoother unless overhaul instructions are different. No sign of corrosion is permitted.
目视检查所有已完成的孔和已完成的机加工表面是否达到规定的表面粗糙度,并查看它们是否过热。表面质量(如与指定轮廓的局部差异、刻痕、凿痕和划痕)必须符合标准行业惯例。如果零件因过热而变色(如蓝色或深灰色),或者有撕裂、颤动痕迹或裂纹,则零件将无法使用。除非大修说明不同,否则孔的表面粗糙度必须为125微英寸或更光滑。不允许有腐蚀迹象。
B.Solution Preparation — See Table 14. Be sure to use containers that are nonreactive to the solutions.
溶液制备——见表14。请确保使用对溶液没有反应的容器。
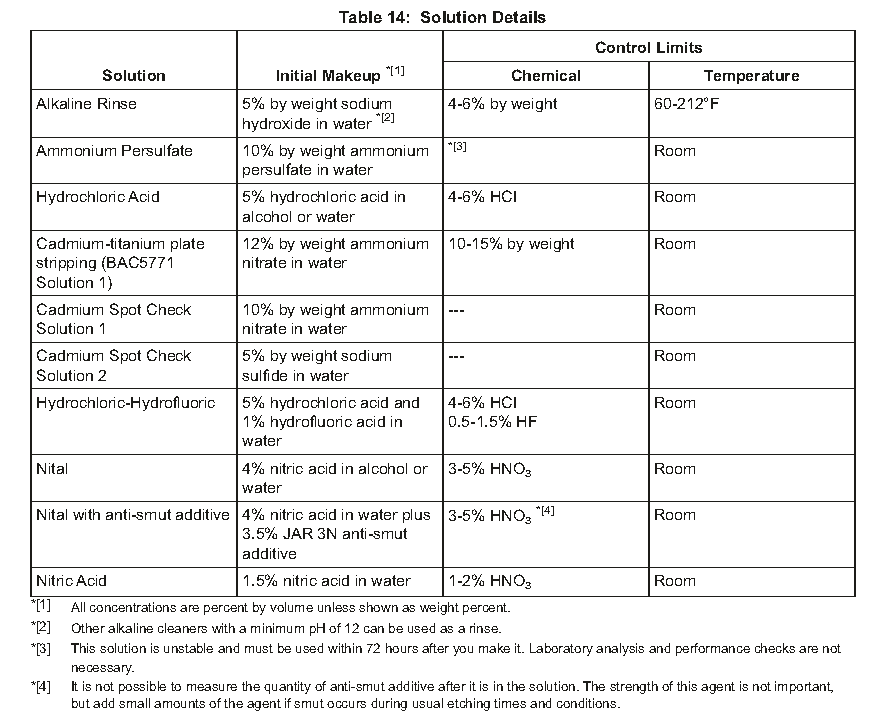
*[1] All concentrations are percent by volume unless shown as weight percent.
*[1] 除非显示为重量百分比,否则所有浓度均为体积百分比
*[2] Other alkaline cleaners with a minimum pH of 12 can be used as a rinse.
*[2] 其他最小pH值为12的碱性清洁剂也可用作漂洗剂
*[3] This solution is unstable and must be used within 72 hours after you make it. Laboratory analysis and performance checks are not necessary.
*[3] 此溶液不稳定,必须在制成后72小时内使用。无需进行实验室分析和性能检查
*[4] It is not possible to measure the quantity of anti-smut additive after it is in the solution. The strength of this agent is not important, but add small amounts of the agent if smut occurs during usual etching times and conditions.
*[4] 在溶液中加入抗污添加剂后,无法测量其数量。这种试剂的强度并不重要,但如果在正常的蚀刻时间和条件下出现污迹,则添加少量试剂。
C.Surface Preparation表面处理
(1)Be sure all plating is removed from the locations to be etch examined. Refer to SOPM 20-30-02 to remove the plating.
确保从待蚀刻检查的位置移除所有镀层。请参阅SOPM 20-30-02以去除镀层。
NOTE: Chemically strip Cadmium (or Cadmium-Titanium) plating to ensure that no residual plating remains prior to Nital Etch. Residual Cadmium (or Cadmium-Titanium) plating causes Nital Etch to be ineffective. Abrasive methods do not completely remove all of the plating and leaves residual behind that may not be readily visible.
注:化学剥离镉(或镉钛)镀层,以确保在Nital蚀刻之前没有残留镀层。残留的镉(或镉钛)镀层会导致Nital蚀刻无效。研磨方法不能完全去除所有镀层,并留下不易看到的残留物。
(2)Vapor degrease or solvent clean or emulsion clean as specified in SOPM 20-30-03.
按照SOPM 20-30-03的规定进行蒸汽脱脂或溶剂清洁或乳液清洁。
(3)To make the etch process work better, we recommend you dry abrasive clean or blast the parts as specified in SOPM 20-30-03, but not on surfaces with a surface finish of 16 microinches or smoother. Use 100-180 grit aluminum oxide, garnet, or size A (170-400 mesh) glass beads. Be careful to make your selection of particle size and blast procedure to keep the surface finish and dimensions constant. Use clean white gloves when you hold or touch the parts. For surfaces with a surface finish of 16 microinches or smoother, do not abrasive clean, but alkaline clean as specified in SOPM 20-30-03.
为了使蚀刻工艺更好,我们建议您按照SOPM 20-30-03的规定对零件进行干磨料清洁或喷砂处理,但不要在表面光洁度为16微英寸或更光滑的表面上进行。使用100-180目的氧化铝、石榴石或尺寸为A(170-400目)的玻璃珠。请小心选择颗粒尺寸和喷砂程序,以保持表面光洁度和尺寸不变。手持或触摸零件时,请使用干净的白色手套。对于表面光洁度为16微英寸或更光滑的表面,不要进行研磨清洁,而是按照SOPM 20-30-03的规定进行碱性清洁。
(4)Alkaline clean as specified in SOPM 20-30-03, or ultrasonic clean as specified in BAC5200. Look for water breaks. Do this step again if water breaks occur. This step is optional if you use the Nital solution, or if you immediately continue with the etch procedure.
SOPM 20-30-03中规定的碱性清洁,或BAC5200中规定的超声波清洁。寻找断水处。如果出现断水现象,请再次执行此步骤。如果使用Nital溶液,或者立即继续蚀刻程序,则此步骤是可选的。
D.Surface Temper Etch (Nital or Aqueous Nitric Acid Solution) — Immersion Method
表面回火蚀刻(硝酸或硝酸水溶液)——浸渍法
WARNING: NITRIC ACID, HYDROCHLORIC ACID, AND SODIUM HYDROXIDE ARE DANGEROUS LIQUIDS. DO NOT BREATHE THEIR VAPORS. DO NOT GET THESE MATERIALS IN EYES, ON SKIN, OR ON CLOTHING
警告:硝酸、盐酸和氢氧化钠是危险的液体。不要吸入它们的蒸汽。不要将这些物质涂在眼睛、皮肤或衣服上
(1)Make these solutions as shown in Table 14.
如表14所示制作这些溶液
a)Nital solution with optional anti-smut additive (all steels but BMS 7-223), or nitric acid solution (BMS 7-223 steels)
含可选防污添加剂的硝酸溶液(除BMS 7-223外的所有钢材)或硝酸溶液(BMS 7-223钢材)
b)Hydrochloric acid solution
盐酸溶液
c)Alkaline rinse solution
碱性冲洗溶液
(2)Nital Etch ProcedureNital
蚀刻程序
a)As applicable, put the part in the Nital solution or the nitric acid solution at 60-90°F for 15-40 seconds, or the Nital solution with anti-smut additive for 15-90 seconds.
如适用,将零件放入温度为60-90°F的Nital溶液或硝酸溶液中15-40秒,或放入含有防污添加剂的Nital溶剂中15-90秒。
b)Rinse in hot or cold water or alcohol.
用热水或冷水或酒精冲洗。
c)Blow off the water immediately. The parts can be wet but must not contain pockets of water.
立即把水吹净。零件可以是湿的,但不能有积水。
d)If you used the anti-smut additive, do not do this step, but go directly to the next step. If you did not use the anti-smut additive, put the part in the hydrochloric acid solution at room temperature (approximately 60-90°F) for 30-60 seconds, rinse in hot or cold water or alcohol, then blow off the water immediately. The part can be wet but must not contain pockets of water.
如果您使用了防污添加剂,请不要执行此步骤,而是直接进入下一步。如果未使用防污添加剂,请将零件置于室温(约60-90°F)下的盐酸溶液中30-60秒,用热水或冷水或酒精冲洗,然后立即把水吹净。零件可以是湿的,但不能有积水。
e)Rinse in the alkaline rinse solution at 60-212°F for 15 seconds minimum with agitation.
在60-212°F的碱性冲洗溶液中搅拌至少15秒。
f)Rinse in hot water at 130-180°F.
在130-180°F的热水中冲洗。
g)Blow dry with clean, dry air.
用干净、干燥的空气吹干。
h)Examine the part under bright light (200 foot candles minimum) without magnification for signs of heat damage. Refer to Paragraph 11.F. for interpretation of etch results.
在明亮光线(至少200英尺烛光)下不使用放大镜检查零件是否有热损伤迹象。有关蚀刻结果的说明,请参阅第11.F.段。
(3)After Inspection检查后程序
a)If you used the anti-smut additive, do not do this step, but go directly to the next step. If you did not use the anti-smut additive, do a hydrogen embrittlement relief bake at 350-400°F for 3 hours minimum. This bake can be combined with the stress relief as specified in Paragraph 10.A.(3).
如果您使用了防污添加剂,请不要执行此步骤,而是直接进入下一步。如果您没有使用防污添加剂,请在350-400°F的温度下进行至少3小时的氢脆消除烘烤。这种烘烤可以与第10.A(3)段中规定的应力消除相结合。
b)Give the part protection from corrosion with MIL-PRF-21260 oil or as specified in SOPM 20-44-02, Type 3, Class 2 unless magnetic particle check (next step) follows within 60 minutes.
除非在60分钟内进行磁粉检查(下一步),否则应使用MIL-PRF-21260油或按照SOPM 20-44-02第3类第2类的规定保护零件不受腐蚀。
c)Magnetic particle examine the part as specified in SOPM 20-20-01.
按照SOPM 20-20-01的规定对零件进行磁粉检测。
d)Apply MIL-C-11796, Class 3 corrosion preventive compound or MIL-PRF-7870 oil.
使用MIL-C-11796,3级防腐化合物或MIL-PRF-7870油。
e)Do all other finishing operations specified by the overhaul instructions such as shot peening, honing, lapping, and plating after the etch operations are completed.
蚀刻操作完成后,执行大修说明中规定的所有其他表面处理操作,如喷丸、珩磨、研磨和电镀。
E.Local Etch of Large Parts
大型零件的局部蚀刻
(1)Local Nital Etch Procedure
局部Nital蚀刻程序
a)This procedure can be used for local etch of very large parts, repaired surfaces, or parts which cannot be baked after the etch. The local swab with Nital (with or without the desmutting additive) is preferred because it is more sensitive and less reactive, but you can use the ammonium persulfate procedure as an alternative.
此程序可用于非常大的零件、修复表面或蚀刻后无法烘焙的零件的局部蚀刻。首选使用Nital(含或不含去污垢添加剂)的局部拭子,因为它更敏感,反应性更低,但您可以使用过硫酸铵程序作为替代方案。
b)No bake for hydrogen embrittlement relief is necessary with this procedure.
此程序无需烘烤以消除氢脆。
c)Make these solutions as shown in Table 14:
如表14所示制作这些溶液:
1)Nital solution with anti-smut additive
含防污添加剂的Nital溶液
2)Cadmium-titanium stripping solution
镉钛剥离溶液
3)Alkaline rinse solution
碱性冲洗溶液
4)Cadmium spot check solutions 1 and 2
镉斑点检查溶液1和2
d)Surface preparation表面预处理
1)If applicable, mask off all areas not to be etched
如果适用,遮盖所有不需要蚀刻的区域
2)With the cadmium-titanium stripping solution, chemically remove the plating in the area to be etch examined.
使用镉钛剥离溶液,化学去除待蚀刻检查区域的镀层。
3)To make sure all of the plating is removed, use the cadmium spot check solutions. Put a drop of Solution 1 on the test spot and let it stay for approximately 30 seconds. Soak up the liquid drop onto a piece of filter paper. Add a drop of Solution 2 to the filter paper. If this becomes yellow, there is remaining cadmium on the surface of the part.
为了确保去除所有镀层,请使用镉斑点检查溶液。将一滴溶液1滴在测试点上,静置约30秒。把液滴浸泡在一张滤纸上。在滤纸上滴一滴溶液2。如果变成黄色,则表示零件表面仍有镉残留。
4)Do Paragraph 11.C. steps.(1)(2)(3) until the plating is completely removed.
执行第11.C段的步骤(1) (2)(3)直到镀层被完全去除。
e)Etch Procedure
蚀刻程序
1)Apply Nital etch solution at room temperature smoothly and continuously with a saturated piece of cheesecloth or equivalent for 15-40 seconds. The surface to be etched at one time must not be larger than a 4-inch square or equivalent area. Be sure to rub continuously, to remove the smut made by the etch procedure. Also, do not use hydrochloric acid to try to remove the smut, because this acid could damage the parts by hydrogen embrittlement.
在室温下,用饱和粗棉布或等效物平稳连续地涂抹Nital蚀刻溶液15-40秒。一次蚀刻的表面不得大于4平方英寸或同等面积。一定要连续摩擦,以去除蚀刻过程中产生的污垢。此外,不要使用盐酸来去除污垢,因为这种酸可能会因氢脆而损坏零件。
2)Rinse immediately in hot or cold water or alcohol.
立即用热水或冷水或酒精冲洗。
3)Apply alkali solution with a swab to neutralize the etch solution.
用棉签涂抹碱性溶液以中和蚀刻溶液。
4)Rinse immediately with hot or cold water or alcohol.
立即用热水或冷水或酒精冲洗。
5)Blow dry immediately with clean, dry air.
立即用干净、干燥的空气吹干。
6)Examine the part under bright light (200 foot candles minimum) without magnification for signs of heat damage. Refer to Paragraph 11.F. for interpretation of results.
在明亮光线(至少200英尺烛光)下不使用放大镜检查零件是否有热损伤迹象。有关结果的解释,请参阅第11.F.段。
f)After inspection
检查后程序
1)Apply MIL-C-11796, Class 3 corrosion preventive compound or MIL-PRF-7870 oil.
使用MIL-C-11796,3级防腐化合物或MIL-PRF-7870油。
2)Do all other finishing operations specified by the overhaul instructions such as shot peening, honing, lapping, and plating after the etch operations are completed.
蚀刻操作完成后,执行大修说明中规定的所有其他精加工操作,如喷丸、珩磨、研磨和电镀。
(2)Optional Local Ammonium Persulfate Etch Procedure
可选的局部过硫酸铵蚀刻程序
WARNING:AMMONIUM PERSULFATE IS AN OXIDIZER AND AN IRRITANT. IT CAN CAUSE FIRE OR EXPLOSION IF MIXED WITH FLAMMABLE MATERIALS AND CAN START A FIRE IN ORGANIC MATERIALS. USED SWABS COULD CAUSE A FIRE OR EXPLOSION. THIS COMPOUND CAN BURN THE SKIN. KEEP THIS COMPOUND AWAY FROM SKIN, EYES, OR CLOTHING. IMMEDIATELY FLUSH THE COMPOUND FROM THE SKIN OR EYES WITH A FLOW OF WATER, AND GET MEDICAL HELP.
警告:过硫酸铵是一种氧化剂和刺激物。如果与易燃材料混合,它可能会引起火灾或爆炸,并可能在有机材料中引发火灾。使用过的棉签可能会引发火灾或爆炸。这种化合物会灼伤皮肤。使这种化合物远离皮肤、眼睛或衣服。立即用水流冲洗皮肤或眼睛上的化合物,并寻求医疗帮助。
a)This procedure does not require a bake for hydrogen relief after the etch.
该程序不需要在蚀刻后进行烘烤以释放氢气。
b)Make these solutions as shown in Table 14.
如表14所示制作这些溶液。
1)Ammonium persulfate solution.
过硫酸铵溶液。
2)Alkaline rinse solution.
碱性冲洗溶液。
3)Cadmium-titanium-plate stripping solution.
镉钛板剥离液。
4)Cadmium spot check solutions 1 and 2.
镉斑检查溶液1和2。
c)Surface Preparation
表面预处理
1)If applicable, mask off all areas not to be etched.
如果适用,遮盖所有不需要蚀刻的区域。
2)With the cadmium-titanium stripping solution, chemically remove the plating in the area to be etch examined.
使用镉钛剥离溶液,化学去除待蚀刻检查区域的镀层。
3)To make sure all of the plating is removed, use the cadmium spot check solutions. Put a drop of Solution 1 on the test spot and let it stay for approximately 30 seconds. Soak up the liquid drop onto a piece of filter paper. Add a drop of Solution 2 to the filter paper. If this becomes yellow, there is remaining cadmium on the surface of the part.
为了确保去除所有镀层,请使用镉斑检查溶液。将一滴溶液1滴在测试点上,静置约30秒。把液滴浸泡在一张滤纸上。在滤纸上滴一滴溶液2。如果变成黄色,则表示零件表面仍有镉残留。
4)Do Paragraph 11.C. steps (1) thru (3) again until the plating is completely removed.
再次执行第11.C段的步骤(1)至(3),直到镀层完全去除。
d)Ammonium Persulfate Etch Procedure
过硫酸铵蚀刻程序
CAUTION:DO NOT LET THE SOLUTION TOUCH THE CADMIUM PLATED AREAS.
注意:不要让溶液接触镀镉区域。
1)Apply ammonium persulfate solution at room temperature smoothly and continuously with a saturated piece of cheesecloth or equivalent material for 30-60 seconds.
在室温下,用饱和的粗棉布或同等材料平稳连续地涂抹过硫酸铵溶液30-60秒。
2)Rinse immediately in hot or cold water or alcohol.
立即用热水或冷水或酒精冲洗。
3)Apply alkaline rinse solution with a swab to neutralize the etch solution.
用棉签涂抹碱性冲洗溶液以中和蚀刻溶液。
4)Rinse immediately in hot or cold water or alcohol.
立即用热水或冷水或酒精冲洗。
5)Blow dry immediately with clean, dry air.
立即用干净、干燥的空气吹干。
6)Examine the part under bright light (200 foot candles minimum) without magnification for signs of heat damage. Refer to Paragraph 11.F. for interpretation of etch results.
在明亮光线(至少200英尺烛光)下不使用放大镜检查零件是否有热损伤迹象。有关蚀刻结果的解释,请参阅第11.F.段。
e)After inspection
检查后程序
1)Apply MIL-C-11796, Class 3 corrosion preventive compound or MIL-PRF-7870 oil.
使用MIL-C-11796,3级防腐化合物或MIL-PRF-7870油。
2)Do all other finishing operations specified by the overhaul instructions such as shot peening, honing, lapping, and plating after the etch operations are completed.
蚀刻操作完成后,执行大修说明中规定的所有其他精加工操作,如喷丸、珩磨、研磨和电镀。
F.Interpretation of Results
结果解释说明
(1) Unburned areas of an etched part will be a constant gray or black color without reflections when cleaned and etched. This color change is not a problem and can be removed with fine aluminum oxide abrasive cloth.
清洁和蚀刻时,蚀刻零件的未燃烧区域将是不变的灰色或黑色,没有反射。这种颜色变化不是问题,可以用细氧化铝砂布去除。
(2) Retempering burns (overtempered martensite) will show as darker areas on the etched part. This indicates that the surface temperature was hotter than the normal tempering temperature of the material during grinding or machining operations and will result in local softening of the surface material. Retempering burns on through-hardened material in the lower heat treat ranges, 180 to 220 ksi, will not be easy to see because the original tempering temperature is sufficiently high that all etched areas will be dark in color. This type of burn usually results in decreased strength and fatigue life.
再回火烧伤(过回火马氏体)将显示为蚀刻部分的较暗区域。这表明在研磨或机加工操作期间,表面温度比材料的正常回火温度更高,并将导致表面材料的局部软化。在较低的热处理范围(180-220 ksi,)内,穿透硬化材料上的再回火燃烧将不容易看到,因为原始回火温度足够高,所有蚀刻区域都将是深色的。这种类型的烧伤通常会导致强度和疲劳寿命下降。
(3)Rehardening burns (untempered martensite) will show as white or light-colored areas on the etched part. Such burns will normally be surrounded by a black retempered area of overtempered martensite. This indicates that the surface temperature was hotter than the austenite transformation temperature of the material during grinding or machining operations. This type of burn results in local hardened areas of untempered martensite which will usually decrease the fatigue life and toughness of the part, and increased risk of hydrogen embrittlement and stress corrosion.
再硬化烧伤(未回火马氏体)将在蚀刻部分显示为白色或浅色区域。这种烧伤通常会被过热马氏体的黑色再回火区域包围。这表明在研磨或机加工操作期间,表面温度比材料的奥氏体转变温度更高。这种类型的燃烧会导致未回火马氏体的局部硬化区域,这通常会降低零件的疲劳寿命和韧性,并增加氢脆和应力腐蚀的风险。
(4)Ground surfaces of carburized parts that are deficient in carbon or have had too much material removed during grinding will appear light in color when compared to an unburned sample with normal case carbon content.
与具有正常情况下碳含量的未燃烧样品相比,在研磨过程中碳不足或去除过多材料的渗碳零件的研磨表面将呈现浅色。
(5)A metallurgist can help when you are not sure about the results of the etch. The Barkhausen inspection (BAC 5653) can also help.
当你不确定蚀刻的结果时,冶金学家可以提供帮助。Barkhausen检查(BAC 5653)也可以提供帮助。