电刷电镀、阳极氧化和电化学蚀刻BRUSH PLATING, ANODIZING AND ELECTROCHEMICAL ETCHING
1. INTRODUCTION 介绍
A. The data in this subject comes from Boeing Process Specification BAC 5849. The airline has a copy of the Boeing Process Specification.
本主题中的数据来自波音工艺规范 BAC 5849。航空公司拥有波音工艺规范的副本。
B. The data is general. It is not about all situations or specific installations. Use this data as a guide to help you write minimum standards.
数据是通用的。并不涉及所有情况或特定安装。请将此数据作为指南,帮助您编写最低标准。
C. Refer to SOPM 20-00-00 for a definition of standard industry practices, vendor names and addresses, and an explanation of the True Position Dimensioning symbols used.
请参阅 SOPM 20-00-00,了解标准行业惯例的定义、供应商名称和地址以及所使用的真实位置标注符号的解释。
2. SCOPE 范围
A. This document establishes the requirements for deposition of electrolytically formed coatings applied to metal substrates by brush (contact) plating or anodizing as a rework process or as original manufacture, and for manual electrochemical etching prior to penetrant inspection. The process is ideally suited for “in place” treatment of hardware.
本文件规定了通过电刷(接触)电镀或阳极氧化作为返修工序或原始制造应用于金属基材的电解形成涂层的沉积要求,以及渗透检查前的手工电化学蚀刻要求。该工艺非常适合对硬件进行 “就地 ”处理。
NOTE: Do not apply the procedures to high strength steels. If you do not obey, it could cause hydrogen embrittlement of the steel.
注意: 请勿将程序应用于高强度钢。如果不遵守,会导致钢材氢脆。
B. Procedures described in this document are not applicable to any electrically formed coating on low alloy steels heat treated to 220 ksi and above or PH CRES alloys (Custom 465) heat treated to 240 ksi and above. Use SOPM 20-42-10 to apply low hydrogen embrittlement stylus cadmium plating or BAC 5664 to apply low hydrogen embrittlement stylus zinc-nickel alloy plating on low alloy steels heat treated to 220 ksi and above.
本文件中描述的程序不适用于热处理至 220 ksi 及以上的低合金钢或热处理至 240 ksi 及以上的 PH CRES 合金(定制 465)上的任何电成形涂层。使用 SOPM 20-42-10 在热处理至 220 ksi 及以上的低合金钢上进行低氢脆触针镉电镀,或使用 BAC 5664 在热处理至 220 ksi 及以上的低合金钢上进行低氢脆触针锌镍合金电镀。
C. Procedures in this document comply with the requirements of MIL-DTL-865.
本文件之程序符合 MIL-DTL-865 之要求。
3. MATERIALS CONTROL 材料控制
A. Deliverable Materials:
交付材料:
(1) Only the following deliverable materials must be incorporated into the part as specified in Paragraph 9., of this specification.
只有下列可交付材料必须按照本规范第 9.段的规定纳入零件中。
(2) For deliverable materials definition refer to Paragraph 8.
有关可交付材料之定义,请参阅第 8 段。
B. Plating Solutions
电镀溶液
(1) Cadmium Plating Solutions:
电镀镉溶液:
(a) LDC-4802 Cadmium Alkaline; BMS10-132, Type 3, V57868.
LDC-4802 碱性镉;BMS10-132,类型 3,V57868。
(b) LDC-4803 Cadmium S (No Bake); BMS10-132, Type 4, V57868.
LDC-4803 S镉(无烘烤);BMS10-132,类型 4,V57868。
(c) Sifco Process Cadmium Acid, 2020/5050; BMS10-132, Type 5, V11924.
Sifco 工艺镉酸,2020/5050;BMS10-132,类型 5,V11924。
(d) Sifco Process Cadmium (No Bake) Code 2023; BMS10-132, Type 6, V11924.
Sifco 加工镉(无烘烤)代码 2023;BMS10-132,类型 6,V11924。
(e) Sifco Process Solution Cadmium LHE, 5070; BMS10-132, Type 7, V11924.
Sifco 工艺溶液镉 LHE,5070;BMS10-132,类型 7,V11924。
(2) Cobalt Plating Solutions:
电镀钴溶液:
(a) LDC-2701 Cobalt; BMS10-132, Type 9, V57868.
(b) Sifco Process Cobalt (Heavy Built), 2043; BMS10-132, Type 10, V11924.
(c) Sifco Process Cobalt, 5200; BMS10-132, Type 11, V11924.
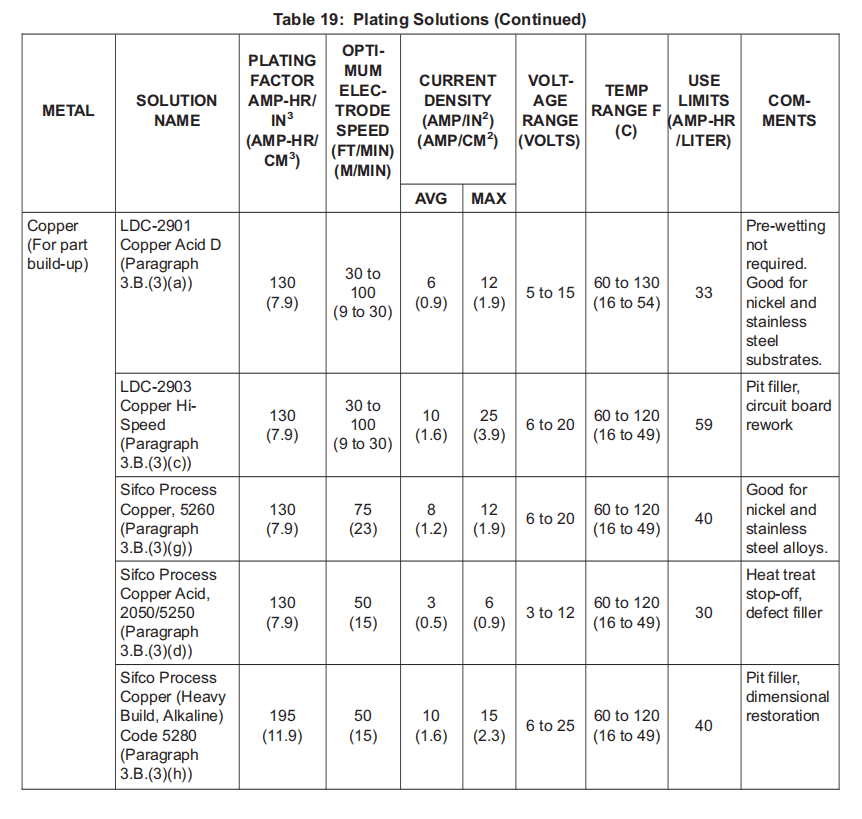
(3) Copper Plating Solutions:
电镀溶液:
(a) LDC-2901 Copper Acid D; BMS10-132, Type 14, V57868
LDC-2901 铜酸 D;BMS10-132,14 型,V57868
(b) LDC-2902 Copper Alkaline; BMS10-132, Type 15, V57868.
LDC-2902 碱性铜;BMS10-132,15 型,V57868。
(c) LDC-2903 Copper Hi-Speed; BMS10-132, Type 16, V57868.
LDC-2903 高速铜;BMS10-132,16 型,V57868。
(d) Sifco Process Copper Acid, 2050/5250; BMS10-132, Type 17, V11924.
Sifco工艺铜酸,2050/5250;BMS10-132,类型 17,V11924。
(e) Sifco Process Copper (High Speed Acid), 2055; BMS10-132, Type 18, V11924.
Sifco 工艺铜(高速酸),2055;BMS10-132,类型 18,V11924。
(f) Sifco Process Copper (High Speed Alkaline), 2056; BMS10-132, Type 19, V11924.
Sifco 工艺铜(高速碱性),2056;BMS10-132,19 型,V11924。
(g) Sifco Process Copper, 5260; BMS10-132, Type 20, V11924.
Sifco 工艺铜,5260;BMS10-132,类型 20,V11924。
(h) Sifco Process Copper (Heavy Build, Alkaline) Code 5280; BMS10-132, Type 21, V11924.
Sifco 工艺铜(重型,碱性)代码 5280;BMS10-132,类型 21,V11924。
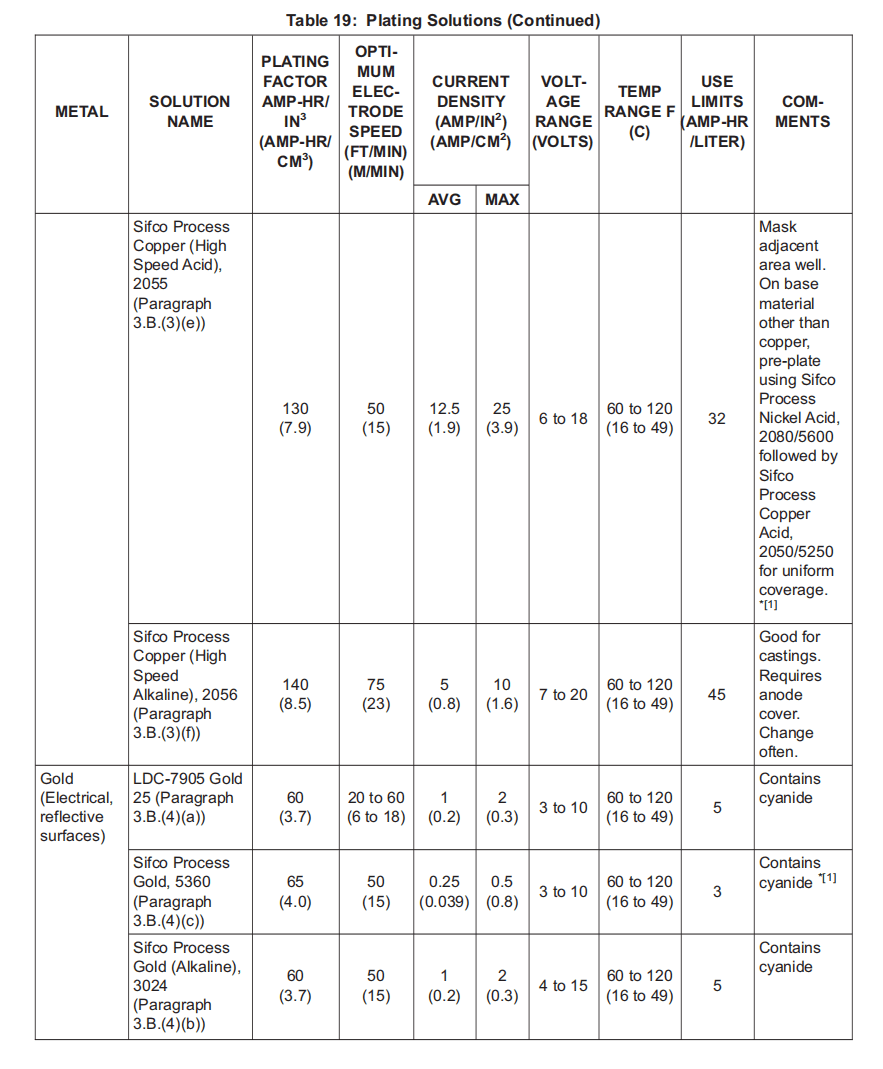
(4) Gold Plating Solutions:
电镀溶液:
(a) LDC-7905 Gold 25; BMS10-132, Type 23, V57868.
LDC-7905 金 25;BMS10-132,类型 23,V57868。
(b) Sifco Process Gold (Alkaline), 3024; BMS10-132, Type 24, V11924.
Sifco工艺金(碱性),3024;BMS10-132,类型 24,V11924。
(c) Sifco Process Gold, 5360; BMS10-132, Type 25, V11924.
Sifco 工艺金,5360;BMS10-132,类型 25,V11924。
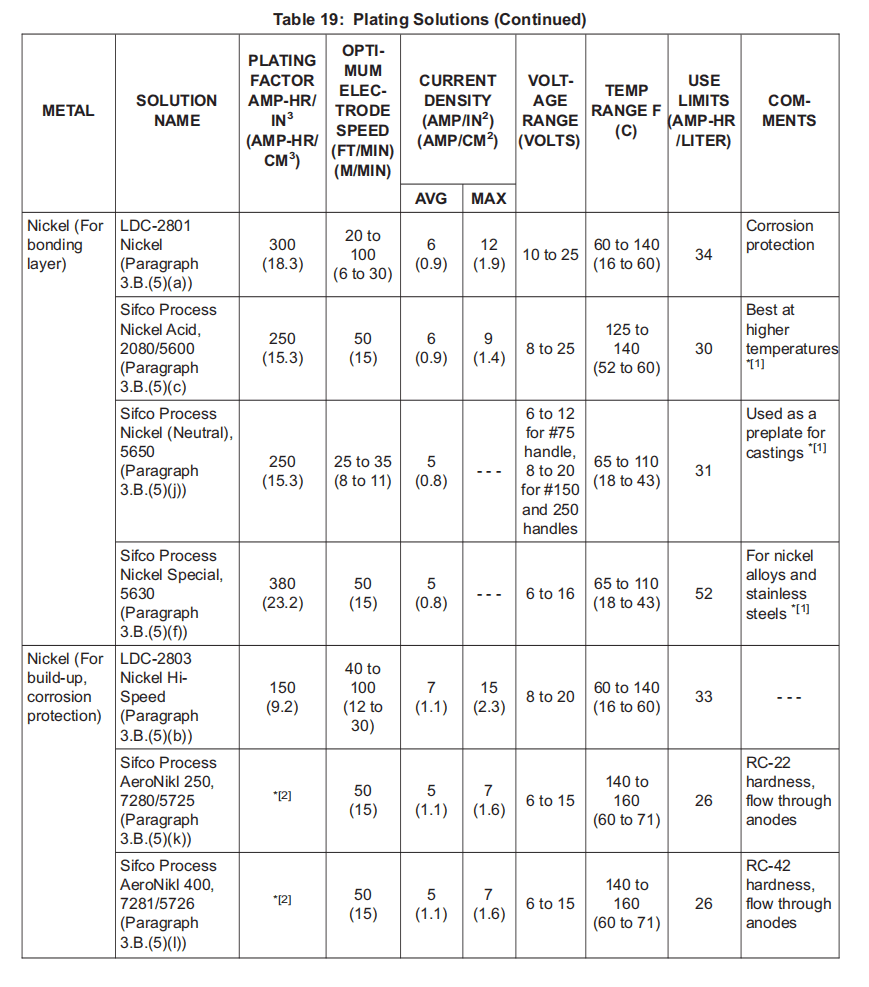
(5) Nickel Plating Solutions:
镍电镀溶液:
(a) LDC-2801 Nickel; BMS10-132, Type 29, V57868.
(b) LDC-2803 Nickel Hi-Speed; BMS10-132, Type 30, V57868.
(c) Sifco Process Nickel Acid, 2080/5600; BMS10-132, Type 31, V11924.
(d) Sifco Process Nickel (High Speed), 2085; BMS10-132, Type 32, V11924.
(e) Sifco Process Nickel (High Temperature), 5610; BMS10-132, Type 33, V11924.
(f) Sifco Process Nickel Special, 5630; BMS10-132, Type 34, V11924.
(g) Sifco Process Nickel (Acid, Heavy Build), 5640; BMS10-132, Type 35, V11924.
(h) Sifco Process Nickel (High Speed), 5644; BMS10-132, Type 36, V11924.
(i) Sifco Process Nickel XHB, 5646; BMS10-132, Type 37, V11924.
(j) Sifco Process Nickel (Neutral), 5650; BMS10-132, Type 38, V11924.
(k) Sifco Process AeroNikl 250, 7280/5725; BMS10-132, Type 39, V11924.
(l) Sifco Process AeroNikl 400, 7281/5726; BMS10-132, Type 40, V11924.
(m) Sifco Process AeroNikl 575, 7282/5727; BMS10-132, Type 41, V11924.
(6) Nickel-Tungsten Plating Solutions:
镍钨电镀溶液:
(a) Sifco Process Nickel-Tungsten D, 5710; BMS10-132, Type 43, V11924.
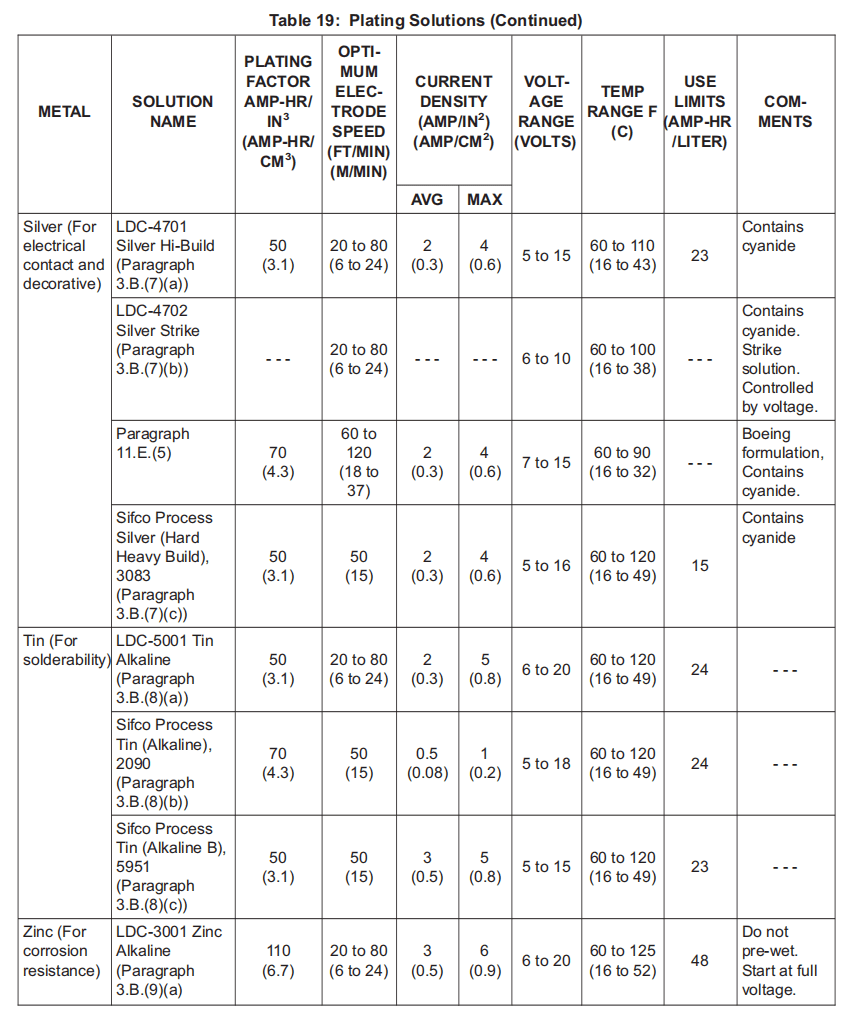
(7) Silver Plating Solutions:
电镀银溶液:
(a) LDC-4701 Silver Hi-Build; BMS10-132, Type 45, V57868.
(b) LDC-4702 Silver Strike; BMS10-132, Type 46, V57868.
(c) Sifco Process Silver (Hard Heavy Build), 3083; BMS10-132, Type 47, V11924.
(8) Tin Plating Solutions:
电镀锡溶液:
(a) LDC-5001 Tin Alkaline; BMS10-132, Type 49, V57868.
(b) Sifco Process Tin (Alkaline), 2090; BMS10-132, Type 50, V11924.
(c) Sifco Process Tin (Alkaline B), 5951; BMS10-132, Type 51, V11924.
(9) Zinc Plating Solutions:
电镀锌溶液:
(a) LDC-3001 Zinc Alkaline; BMS10-132, Type 53, V57868.
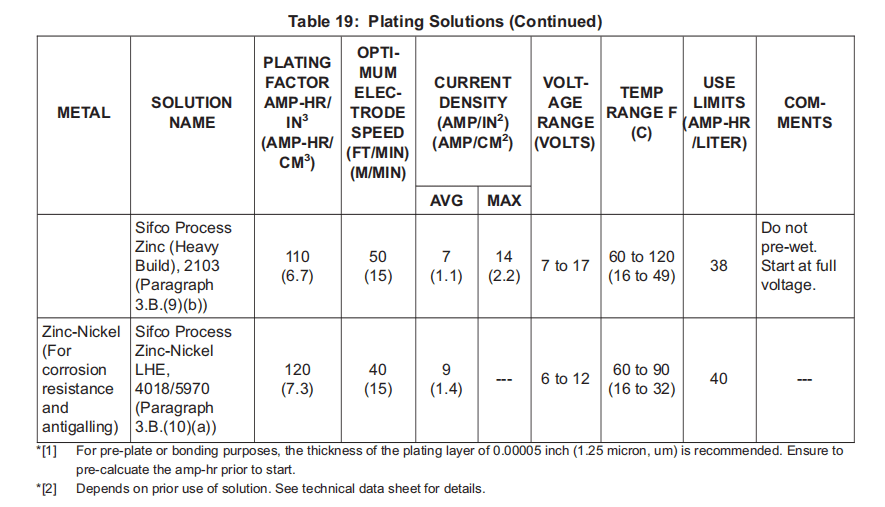
(b) Sifco Process Zinc (Heavy Build), 2103; BMS10-132, Type 54, V11924.
(10) Zinc-Nickel Plating Solutions:
锌镍电镀溶液:
(a) Sifco Process Zinc-Nickel LHE, 4018/5970; BMS10-132, Type 55, V11924.
(11) Chemicals:
化学品:
(a) Silver cyanide; BSI BS 1561.
C. Contact Materials
接触材料
(1) The following non-deliverable materials are specifically called out in Paragraph 9.
第 9 段特别列出以下不可交付的材料。
(2) For contact materials definition refer to Paragraph 8. They are used in contact with production hardware or deliverable material as specified in Paragraph 9.
接触材料的定义见第 8 段。它们用于与第 9 段规定的生产硬件或可交付材料接触。
D. Preplate Preparation and Etching Solutions
预制板制备和蚀刻溶液
(1) LDC-01 Electroclean, V57868.
(2) LDC-02 Activator & Etch, V57868.
(3) LDC-03 Activator & Etch, V57868.
(4) LDC-04 Activator & Etch, V57868.
(5) LDC-06 Hard Chrome Activator, V57868.
(6) Sifco Process Electrocleaning, 1010/4100, V11924.
(7) Sifco Process No. 1 Etching & Activating, 1021/4200, V11924.
(8) Sifco Process No. 2 Etching, 1022/4300, V11924.
(9) Sifco Process No. 3 Etching & Desmutting, 1023, V11924.
(10) Sifco Process No. 3 Etching & Desmutting, 4350, V11924.
(11) Sifco Process No. 4 Etching & Activating, 1024/4250, V11924.
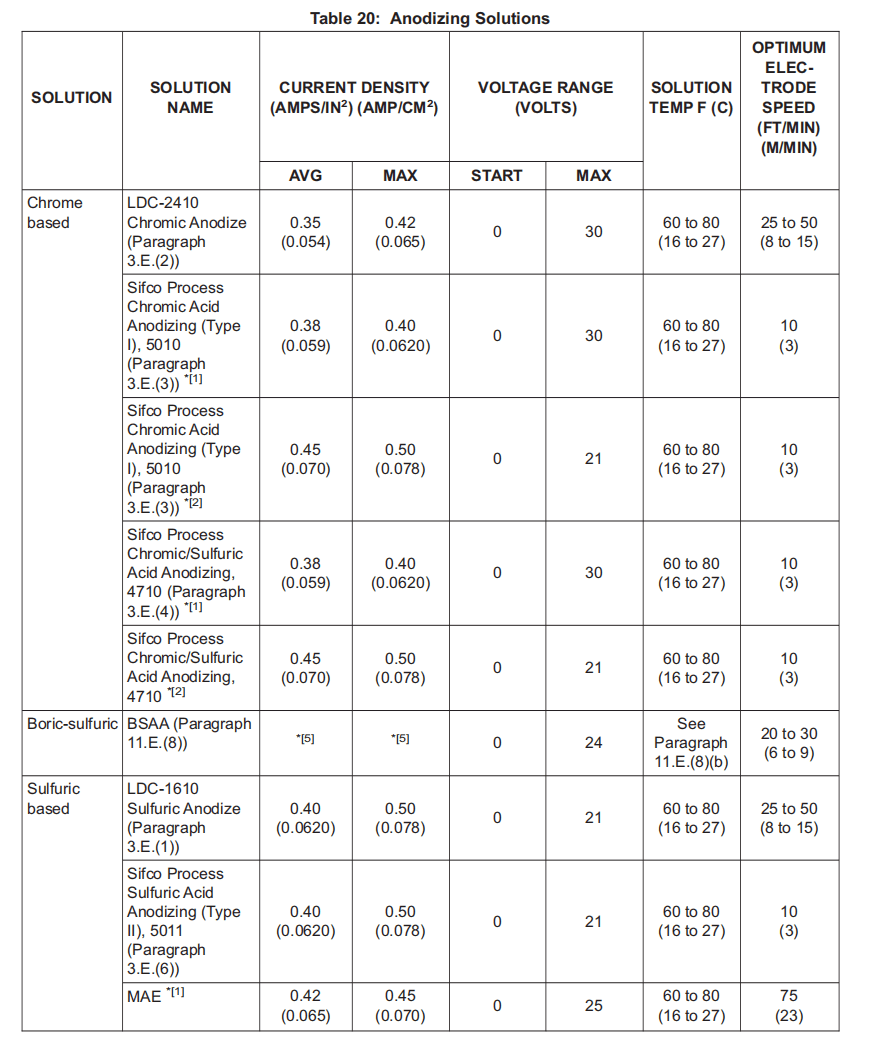
E. Anodizing Solutions
阳极氧化溶液
(1) LDC-1610 Sulfuric Anodize, V57868.
(2) LDC-2410 Chromic Anodize, V57868.
(3) Sifco Process Chromic Acid Anodizing (Type I), 5010, V11924.
(4) Sifco Process Chromic/Sulfuric Acid Anodizing, 4710, V11924.
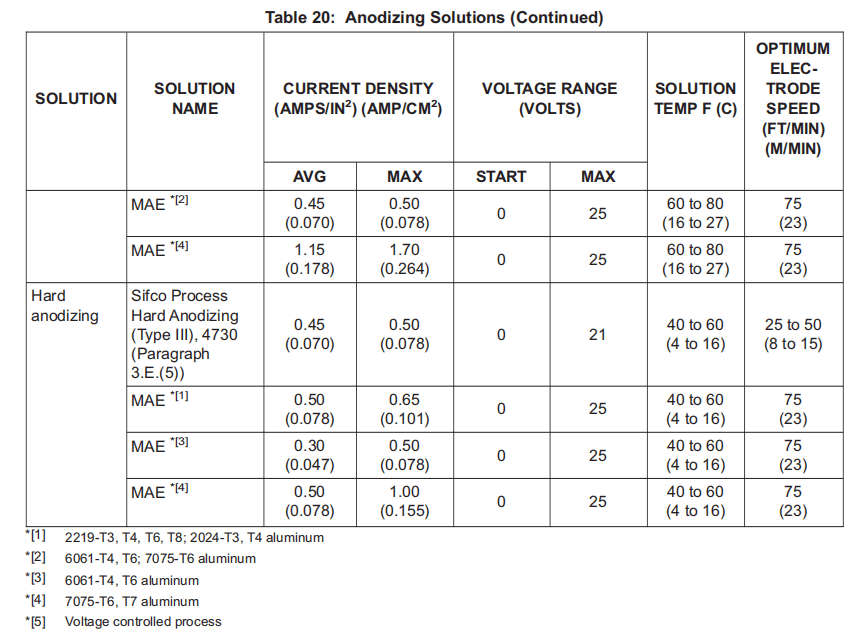
(5) Sifco Process Hard Anodizing (Type III), 4730, V11924.
(6) Sifco Process Sulfuric Acid Anodizing (Type II), 5011, V11924.
F. Stripping Solutions
剥离溶液
(1) LDC-08 Copper & Cobalt Strip, V57868.
(2) LDC-09 Nickel Strip, V57868.
(3) LDC-16 Cadmium, Tin & Zinc Strip, V57868.
G. Conversion Coating (Postplate Treatment) Solutions
转换涂层(镀后处理)溶液
(1) Henkel Corp Bonderite M-CR 600 Aero, V84063.
(2) Henkel Corp Bonderite M-CR 600 RTU Aero, V84063. (This is a premixed solution, ready to be used as supplied by the manufacturer. 这是一种预混合溶液,可按制造商提供的方法使用。)
(3) Henkel Corp Bonderite M-CR 1001 Aero, V84063.
(4) Sifco Process Dichromate Conversion Coating, 1720, V57868.
(5) MacDermid Iridite 80, V0PX54.
(6) MacDermid Iridite 8P, V0PX54.
(7) Sifco Process Chromate (hexavalent) Conversion Coating, 5030/3004, V11924.
(8) Sifco Process Chromate Conversion Coating, 5005.
H. Chemicals
化学品
(1) Boric acid; 99.8 percent minimum as H3BO3 200 ppm maximum chloride.
(2) Chromium trioxide; A-A-55827, Type I or II.
(3) Glycerin, technical grade, 96 percent.
(4) Glycolic acid, technical grade or better, 70 percent.
(5) Magnesium chromate pentahydrate, technical grade or better.
(6) Nitric acid; A-A-59105.
(7) Potassium carbonate, anhydrous, technical.
(8) Potassium chromate, anhydrous, technical grade or better.
(9) Potassium cyanide; plating grade, 98 percent KCN minimum.
(10) Sodium chromate, anhydrous, technical grade or better.
(11) Sodium dichromate dihydrate; A-A-59123.
(12) Sodium hydroxide, technical grade or better, flake or granulated.
(13) Stepan Nacconol 90G.
(14) Sulfuric acid; A-A-55828, Type I, Class 1.
NOTE: Type II, Class 1 may be used if the volume is adjusted to result in the correct solution concentration.
注: 如调整体积以得到正确的溶液浓度,可使用 II 类 1 级。
I. Masking Materials
遮蔽材料
(1) 3M Aluminum Foil Tape 425, V76381.
(2) 3M Lead Foil Tape 420, V76381.
(3) 3M Polyurethane Protective Tape 8560, V76381.
(4) 3M Polyurethane Protective Tape 8562, V76381.
(5) AC Products AC-828-T.
(6) AC Products AC-828-T-Dark Blue.
(7) AC Products AC-850-TCA-TAN.
(8) Evans Stripcoat – Type II B-100, V56307.
(9) Bonderite S-MA 522 Aero.
(10) Mask-Off Protex 1321D-3.
(11) Sequoia GSV-1, V3M808.
(12) Sequoia SC-1, V3M808.
(13) Sifco AeroNikl Tape #11601350, V11924.
(14) Sifco Vinyl Tape #11601100, V11924.
(15) Tolber Miccromask, V59460.
(16) Tolber Miccroshield, V59460.
J. Electrode Materials
电极材料
(1) Electrode Cover Materials:
电极罩材料:
NOTE: Materials for electrode covers must be free from residual binders, stiffening agents, and lubricants.
注: 电极罩材料必须无残留粘合剂、硬化剂和润滑剂。
(a) 3M Scotch-Brite Products, 7445, Light Duty Pad, Clean & Finish F SFN, V76381.
(b) 3M Scotch-Brite Products, 7447, General Purpose Pad, V76381.
(c) 3M Scotch-Brite Products, 7448, V76381.
(d) Cotton gauze, long fiber, surgical grade.
(e) Polyester fabric, such as Pellon.
(f) Polyester string or equivalent.
(g) Polypropylene fabric.
(h) Sifco Cotton Sleeving, V11924.
(i) Sifco PermaWrap, V11924.
K. Miscellaneous Materials
杂项材料
(1) Aluminum oxide grit.
(2) Aluminum oxide abrasive paper.
(3) File, metal, any suitable size, shape, and coarseness.
(4) Wipers:
(a) BMS15-5, Class A or B.
(b) AMS3819, Class 1, 2, or 4, Grade A or B, Form 1.
4. NON-CONTACT MATERIALS 非接触材料
NOTE: The following non-contact materials (see Paragraph 8., for definition) are specifically called out in Paragraph 9., and do not directly contact production hardware or deliverable material.
注: 以下非接触材料(定义见第 8.段)在第 9.段中有具体说明,且不直接接触生产硬件或可交付材料。
A. Electrode Materials
电极材料
(1) Electrode Materials for Custom Fabrication:
用于定制制造的电极材料:
(a) Corrosion resistant steel containing 18 percent chromium, minimum, and 8 percent nickel, minimum (for example, AISI 304, AISI 316, and AISI 321 stainless steels).
至少含 18%铬和 8%镍的耐腐蚀钢(例如,AISI 304、AISI 316 和 AISI 321 不锈钢)。
(b) Electrodes and styluses must be made as specified in Paragraph 9.E., or purchased from suppliers of this equipment.
电极和触针必须按第 9.E. 段的规定制造,或从该设备的供应商处购买。
(c) Graphite of high purity and high density. Some suggested sources are as follows: Sifco, Union Carbide, Airco Carbon.
高纯度、高密度的石墨。建议的来源如下 Sifco、Union Carbide、Airco Carbon。
(d) Platinum.
(e) Platinized niobium.
(f) Platinized titanium.
(g) Platinum-iridium.
(h) Preformed electrodes, see commercial brush plating supply catalogs.
(2) Electrode Handles, Stylus, Commercial:
电极手柄,触针,商业
(a) Sifco No. 75 for current to 75 amps, V11924.
(b) Sifco No. 150 for current to 150 amps, V11924.
(c) Sifco No. 250 for current to 250 amps, V11924.
(3) Miscellaneous Materials:
其他材料:
(a) Polyethylene or glass bottles with caps.
带盖的聚乙烯或玻璃瓶。
5. MATERIAL STORAGE CONTROL 材料储存控制
A. Storage temperature and shelf life requirements are given in Table 1 thru Table 16.
储存温度和保质期要求见表 1 至表 16。
B. Each material must be stored within the temperature range shown from date of receipt through date of use.
每种材料自收到之日起至使用之日止,必须储存在所示温度范围内。






C. Prior to use of a material that is beyond its original shelf life on production hardware, requirements are as follows:
在生产硬件上使用超过原保质期的材料之前,须满足以下要求:
(1) The processor is responsible for ensuring that the material complies with all requirements of the material specification as specified in Paragraph 3., Paragraph 4., Paragraph 5. and Paragraph 6.
处理人负责确保材料符合第 3.段、第 4.段、第 5.段和第 6.段规定的材料规格的所有要求。
NOTE: It is recommended that new test data, historical test data, rationale, and/ or experience be utilized to ensure compliance. It is also recommended that the processor consult with the Boeing Specification custodian and supplier of the material if there is uncertainty pertaining to this compliance.
注: 建议利用新的测试数据、历史测试数据、理由和/或经验来确保符合要求。如果不确定是否符合要求,还建议处理人咨询波音规格保管人和材料供应商。
(2) The processor must test the material for compliance with any requirement that specified in Paragraph 3., Paragraph 4., Paragraph 5. and Paragraph 6., if deemed necessary.
如有必要,处理人必须测试材料是否符合第 3 段、第 4 段、第 5 段和第 6 段规定的任何要求。
6. MATERIALS CROSS REFERENCE 材料对照
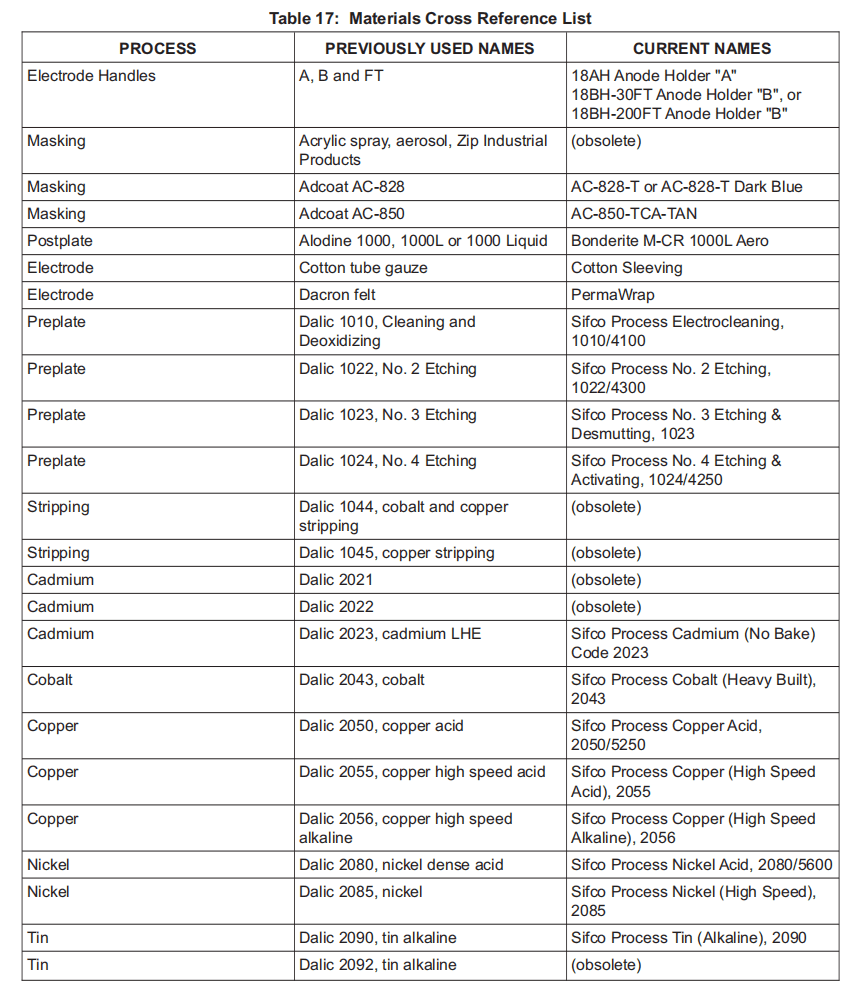
A. Manufacturers have changed the names of some materials, and some materials have become obsolete. Table 17 lists previously used names along with comparable current names or the indication that the material is obsolete.
制造商已更改某些材料的名称,某些材料已废弃。表 17 列出了以前使用的名称,以及目前可比的名称或材料已废弃的说明。
B. Usable quantities of the materials with dual listings remaining after the revision date of this standard may be used until depleted; except do not use Scotch Foam Tape No. 4104 or No. 4116, Industrial Specialties Div, 3M Co.
在本标准修订日期后,仍可使用双重列名材料的可用数量,直至耗尽为止;但不得使用 Scotch 泡沫胶带 4104 号或 4116 号(3M 公司工业特种产品部)。



7. FACILITIES CONTROL 设施控制
A. Power Supplies
电源
(1) Power supplies must provide adjustable DC voltage and an output polarity reversing switch.
电源必须提供可调节的直流电压和输出极性转换开关。
(2) The voltmeter and ammeter must be accurate to ± 5 percent, and calibration is required.
电压表和电流表必须精确到 ± 5%,并需要校准。
NOTE: A-A-59460 may be used as a guide in the selection of power supplies. The recommended readability of an ampere-hour meter is 0.001 amp-hr for power supplies with an output up to 30 amperes, 0.01 amp-hr for power supplies with an output of 31 to 200 amperes, or 0.1 amp-hr for power supplies with an output above 200 amperes. Either fuse or circuit breaker overload protection is recommended in order to prevent serious damage to the part if a direct short occurs. Microprocessors incorporated into the power supplies may be used to estimate variables and nominal operating parameters. It is recommended that the power supply DC voltage output have an AC ripple of 5 percent or less over the entire operating range when measured with a resistive load.
注: A-A-59460 可用作选择电源的指南。对于输出不超过 30 安培的电源,建议安培小时表的可读性为 0.001 安培-小时;对于输出 31 至 200 安培的电源,建议可读性为 0.01 安培-小时;对于输出超过 200 安培的电源,建议可读性为 0.1 安培-小时。建议使用保险丝或断路器过载保护,以防止发生直接短路时对零件造成严重损坏。电源中的微处理器可用于估算变量和额定运行参数。建议电源直流电压输出在使用电阻负载测量时,在整个工作范围内的交流纹波不超过 5%。
B. Auxiliary Equipment
辅助设备
(1) Pumps
泵
NOTE: Peristaltic type pumps, with a variable flow rate of 0 to 4 L/min, are recommended. Submersible, all-plastic pumps may also be used.
注: 建议使用流量为 0 至 4 升/分钟的蠕动泵。也可使用全塑料潜水泵。
(2) Turning Accessories
旋转配件
(a) Turning accessories turn either the electrode or the part.
旋转配件可旋转电极或零件。
NOTE: Continuous variable speed control in both the forward and reverse directions is recommended. Turning accessories, including hand-held rotary tools, flow-through rotary tools, lathes or turning heads, turn tables, etc., can be either commercially procured or fabricated in-house.
注: 建议在正向和反向均采用连续变速控制。车削配件,包括手持式旋转工具、流动式旋转工具、车床或车削头、转台等,可从市场上采购或内部制造。
(3) Cooling/Heating Units
冷却/加热装置
(a) Tanks must be equipped with a calibrated temperature indicating and controlling device located at approximately the mid-temperature region of the work zone.
槽必须配备校准的温度显示和控制装置,其位置大约位于工作区的中温区。
(b) The accuracy of these devices must be ± 3 F (2 C).
这些装置的精确度必须为 ± 3°F (2 C)。
(4) Processing Tools
加工工具
(a) Electrodes and styluses are required. They must be made in accordance with Paragraph 9.E., or purchased from suppliers of this equipment (Paragraph 4.).
需要电极和触针。它们必须按照第 9.E 段制造,或从该设备供应商处购买(第 4.段)。
(b) For anodize rework process support, the following tools must be used. Temperature measuring and controlling devices must be certified to be accurate within ± 2 F (1 C) of indicated readings.
为支持阳极氧化返修工序,必须使用以下工具。温度测量和控制装置须经认证,其准确度在指示读数的 ± 2 °F (1 C) 以内。
1) Constant temperature (0 to 200 F, -18 to 93 C) bath, any supplier.
恒温槽(0 至 200 F,-18 至 93 C),任何供应商提供。
2) Digital thermocouple thermometer (0 to 200 F, -18 to 93 C), any supplier.
数字热电偶温度计(0 至 200 F,-18 至 93 C),任何供应商均可提供。
3) Surface probe adaptable for thermocouple thermometer, any supplier.
适用于热电偶温度计的表面探头,任何供应商均可提供。
NOTE: Suggested: Cole Parmer, Part No. 08506-95
注: 建议使用: Cole Parmer,零件号 08506-95
4) Electric heating blankets, 5 watt maximum
电热毯,最大 5 瓦
5) Temperature Controller
温度控制器
6) Anodize color chips (Paragraph 10.F.(4)(c)).
阳极氧化色片(第 10.F.(4)(c)段)。
(c) Desco continuity tester Model 35100, 35130, or 35135; or any probe approved by BSS7343 for determining the presence of anodize coating.
型号为 35100、35130 或 35135 的 Desco 连续性测试仪;或 BSS7343 批准用于确定阳极氧化涂层是否存在的任何探头。
(5) Compressed Air
压缩空气
(a) Compressed air must be free of oil, moisture and particulate matter when tested in accordance with BSS7217.
根据 BSS7217 进行测试时,压缩空气必须无油、无湿气、无微粒物质。
(6) Water
水
(a) Water used for preparation and maintenance of a plating solution must have an electrical resistivity of not less than 50,000 ohm-cm.
用于配制和维护电镀溶液的水的电阻率须不小于 50,000 欧姆-厘米。
(b) Water used for rinsing must not exceed 750 ppm total solids.
用于漂洗的水总固体含量不得超过 750 ppm。
8. DEFINITIONS 定义
A. The following definitions apply to terms that are uncommon or have special meaning as used in this specification.
以下定义适用于本规范中不常用或有特殊含义的术语。
(1) BSAA – Boric acid-sulfuric acid anodize.
BSAA – 硼酸-硫酸阳极氧化。
(2) Burning – Undesirable condition in which plating becomes discolored and/or rough in high current density areas such as along edges and external corners. The surface being processed can burn when one or more of the following occurs: Improper anode to cathode movement, incorrect solution temperature, excessive voltage, solution contamination, or solution starvation.
烧蚀 – 电镀在高电流密度区域(如边缘和外角)变色和/或粗糙的不良情况。当出现以下一种或多种情况时,正在加工的表面可能会烧焦: 阳极到阴极移动不当、溶液温度不正确、电压过高、溶液污染或溶液饥饿。
(3) Contact material – A material listed as specified in Paragraph 3.C., and used in contact with production hardware or deliverable material as specified in Paragraph 9., of this specification.
接触材料 – 第 3.C.段规定的材料,用于与生产硬件或本规范第 9.段规定的交付材料接触。
(4) Deliverable material – A material listed as such in Paragraph 3.A., and used as specified in Paragraph 9., of this specification and such that any or all components of this material remains on production hardware after completing the Paragraph 9., process.
可交付材料–第 3.A.段所列材料,并按本规范第 9.段规定使用,且在完成第 9.段过程后,该材料的任何或所有部件仍留在生产硬件上。
(5) Electrode – Tool which contacts the part when brush plating or anodizing. When brush plating the electrode is the anode. When anodizing or etching the electrode is the cathode.
电镀 (Electrode) – 电刷镀或阳极氧化时接触零件的工具。电镀时电极为阳极。阳极氧化或蚀刻时,电极为阴极。
(6) Engineering Drawing – The collection of product definition data used to disclose, directly or by reference, through pictorial or textual presentations, or combinations of both, the physical and functional end product requirements and configuration of an item. The term may be used regardless of the actual medium or method used for its depiction. A drawing may be computer-aided, manually produced, digitally defined within a dataset and plotted, or digitally defined within a dataset and not plotted.
工程图–产品定义数据的集合,用于通过图形或文字展示,或两者的组合,直接或通过参考,披露物理和功能上的最终产品要求和项目配置。无论使用何种实际媒介或方法进行描述,均可使用该术语。图纸可由计算机辅助绘制、手工绘制、在数据集内数字定义并绘制,或在数据集内数字定义但不绘制。
(7) Etch Factor – Number of amp-hours required to remove a specified volume of metal.
蚀刻系数 – 去除规定体积金属所需的安培小时数。
(8) Forward current – Current flow direction that is achieved when the processing tool is connected to the positive (+) terminal of the power supply and the part to the negative (-) terminal. Most commercial power supplies designate forward current as PLATE or POSITIVE (+) current direction on the polarity switch.
正向电流 – 当加工工具连接到电源的正极 (+) 端子,而零件连接到负极 (-) 端子时实现的电流流动方向。大多数商用电源在极性开关上将正向电流指定为PLATE或正向 (+) 电流方向。
(9) Non-contact material – A material listed as such in Paragraph 4., and used as indicated in Paragraph 9., of this specification that is not deliverable and does not directly contact production hardware or a deliverable material.
非接触材料 – 在本规范第 4 段中被列为非接触材料并在第 9 段中注明使用的材料,它不是可交付材料,不直接接触生产硬件或可交付材料。
(10) Plating Factor – Number of amp-hours required to deposit a specified volume of metal on a specified area.
电镀系数 – 在规定面积上沉积规定量金属所需的安培小时数。
(11) Reverse current – Current flow direction that is achieved when the processing tool is connected to the negative (-) terminal of the power supply and the part to the positive (+) terminal. Most commercial power supplies designate reverse current as DEPLATE or NEGATIVE (-) current direction on the polarity switch.
反向电流 – 当加工工具连接到电源的负极 (-) 端子,而零件连接到正极 (+) 端子时实现的电流流动方向。大多数商用电源在极性开关上将反向电流指定为DEPLATE或负极(-)电流方向。
(12) Solution-break-free surface – A vertical surface which maintains a continuous solution film for a period of at least 30 seconds either during the last two steps of the electrolytic preplate treatment procedure before plating, or during the water rinse step of the hydroblast preplate treatment procedure before plating.
无溶液断水表面–在电镀前电解预镀处理程序的最后两步,或在电镀前喷水预镀处理程序的水冲洗步骤中,保持连续溶液膜至少 30 秒的垂直表面。
(13) Spent Solution – Solution that either contains a precipitate or contaminants, no longer produces acceptable plating, anodizing, or etching, or has exceeded the manufacturer’s recommended use limit (amp-hours/ liter).
废溶液–含有沉淀物或污染物,不再产生可接受的电镀、阳极 氧化或蚀刻效果,或已超过制造商建议的使用限值(安培小时/升)的溶液。
(14) Type (as designated in MIL-A-8625):
类型(在 MIL-A-8625 中指定):
(a) Type I: conventional coatings produced from a chromic acid bath.
I 型:用铬酸槽生产的常规涂层。
(b) Type II: conventional coatings produced from a sulfuric acid bath.
类型 II:用硫酸槽生产的常规涂层。
(c) Type III: hard anodic coatings.
类型 III:硬阳极涂层。
(15) Used Solution – Solution that has contacted a part or been contacted by a current-on electrode.
使用过的溶液–接触过零件或被电流电极接触过的溶液。
(16) Water-break-free surface – A vertical surface which maintains a continuous water film for a period of at least 30 seconds after having been spray or immersion rinsed in clean water at a temperature below 100 F (38 C).
无断水表面–在温度低于 100°F (38 C)的清水中喷淋或浸泡冲洗后,能在至少 30 秒钟内保持连续水膜的垂直表面。
9. MANUFACTURING CONTROL 生产控制
A. General
通用
(1) For new manufacture, brush plate or anodize in sequence with other manufacturing operations.
对于新制造的产品,电镀或阳极氧化应与其他制造工序依次进行。
NOTE: If processing is done prior to completion of manufacturing operations, protection from subsequent damage to the electroplated or anodized surface is recommended.
注: 如果在制造工序完成之前进行加工,建议采取保护措施,防止电镀或阳极氧化表面随后受到损坏。
NOTE: Prevent silicone contamination. Silicone contamination can prevent subsequent materials from remaining on parts.
注: 防止硅污染。硅污染会妨碍后续材料留在零件上。
(2) Minimize the handling of pretreated metal parts. Handle with gloves such that the outside surface of the gloves is kept clean, dry, and free of lint, powder and silicones. Avoid contact with oily or other contaminated surfaces when using gloves that are being used to handle pretreated metal parts. Change gloves as often as necessary to prevent contamination of the pretreated metal parts.
尽量减少对预处理金属零件的处理。戴手套操作,保持手套外表面清洁、干燥、无绒毛、粉末和有机硅。在使用手套处理预处理过的金属零件时,应避免接触油性或其他受污染的表面。根据需要经常更换手套,以防止预处理过的金属零件受到污染。
NOTE: White or light colored cloth gloves are recommended because they are effective at revealing dark colored contamination. The test method of AMS3819 is recommended for testing new gloves for silicone contamination.
注意:建议使用白色或浅色的布手套,因为它们能有效地揭示深色的污染。推荐AMS3819的测试方法用于检测新手套的硅酮污染。
(3) For rework and “in place” processing, if possible, bring the part to be treated into a manufacturing area set up to do such work. If this is not possible, prepare the part for in place plating or anodizing by taking the following steps and any other steps deemed necessary by the qualified plater.
对于返工和 “就地 ”处理,如果可能,将待处理的零件带入为进行此类工作而设置的制造区。如果不可能,则应采取以下步骤和合格电镀工认为必要的任何其他步骤,为就地电镀或阳极氧化处理零件做好准备。
(a) Secure movable parts to prevent any unwanted or harmful motion, and remove any possible unwanted current paths (for example, through the bearings of a motor or through a power cable).
固定活动零件,防止任何不必要或有害的运动,并清除任何可能的不必要电流路径(例如,通过电机轴承或通过电源电缆)。
(b) Analyze the extent of the rework (for example, area requiring rework, thickness, pits to be filled, extent of corrosion, methods available for corrosion removal, feathering required, masking and damming required, etc.).
分析返工范围(例如,需要返工的面积、厚度、需要填补的凹坑、锈蚀程度、可用的除锈方法、所需的羽化、所需的遮蔽和阻挡等)。
(4) In the process tables where more than one solution is shown as being usable for a specific operation, it is permissible to use any of the solutions listed for the process. However, solutions from only one manufacturer must be used for an entire process.
在工序表中,如果显示有一种以上的溶液可用于特定操作,则允许使用该工序所列的任何一种溶液。但整个工序必须只使用一个制造商生产的溶液。
(5) Use pans, plastic sheeting, or such to catch solution drips and spills. Dispose of the collected solution by an approved method.
使用盘、塑料薄膜等收集溶液的滴漏和溢出。收集到的溶液应按批准的方法处理。
(6) Surfaces must be water-break-free following immersion in any rinse and solution-break-free following immersion in any processing solution, except following vapor degreasing or solvent cleaning. Reclean parts that show any water or solution breaks.
除蒸气脱脂或溶剂清洗外,浸入任何冲洗液的表面必须无断水,浸入任何加工溶液的表面必须无断水溶液。重新清洗有水渍或溶液破损的零件。
(7) Parts must not dry between process steps, unless otherwise noted.
除非另有说明,否则各加工步骤之间的零件不得干燥。
(8) A solution may be used up to the limit of ampere-hours per liter as shown in Table 19 or as specified by the manufacturer or until the solution produces unacceptable plating or anodizing.
溶液可使用至表 19 所示或制造商规定的每升安培小时极限,或直至溶液产生不可接受的电镀或阳极氧化。
(9) A vendor-supplied solution from a container with a precipitate must not be used unless the precipitate has been dissolved and thoroughly mixed into the solution. Do not mix the solution or precipitate with water or any other material in an effort to dissolve a precipitate.
除非沉淀物已溶解并与溶液充分混合,否则不得使用供应商提供的带有沉淀物的溶液。切勿将溶液或沉淀物与水或任何其他材料混合以试图溶解沉淀物。
NOTE: To increase solubility of a precipitate, the solution may be heated to its maximum storage temperature and gently agitated.
注: 为增加沉淀的溶解度,可将溶液加热至最高储存温度并轻轻搅拌。
(10) Unless otherwise specified, brush plating must be applied only after all base metal heat treatment and mechanical operations such as machining, brazing, welding, forming and perforating of the article have been completed.
除非另有规定,电镀必须在所有母材热处理和机械操作(如机械加工、钎焊、焊接、成型和穿孔)完成后方可进行。
B. Process Flow
工艺流程
(1) Preprocess preparation (Paragraph 9.C.):
加工前准备(第 9.C 段):
(2) Preparation of work (Paragraph 10.B.):
准备工作(第 10.B 段):
(a) Electroplating (Paragraph 10.C.).
电镀(第 10.C 段)。
(b) Anodizing of aluminum (Paragraph 10.D.).
铝阳极氧化(第 10.D 段)。
(c) Electrochemical etching (Paragraph 10.E.).
电化学蚀刻(第 10.E 段)。
C. Preprocess Preparation
加工前准备
(1) Before any processing the following must be accomplished:
在进行任何加工之前,必须完成以下工作:
(a) Calculate the ampere-hours required for the operation (Paragraph 9.D.(3)).
计算操作所需的安培小时数(第 9.D.(3)段)。
(b) Select and prepare the electrodes required (Paragraph 9.E.).
选择和准备所需的电极(第 9.E 段)。
(c) Set up the general operation and equipment.
设置通用操作和设备。
D. Useful Calculations
有用的计算
NOTE: There are a number of useful calculations to help control these operations. These calculations are very general and should be used only to approximate the indicated value.
注: 有一些有用的计算有助于控制这些操作。这些计算非常通用,只能用于近似指示值。
(1) Rotational Speed – When using a device for rotating either the part or the electrode, the following formula can be used to calculate the rotations per minute (rpm) of the rotating device:
转速 – 当使用旋转零件或电极的装置时,可使用以下公式计算旋转装置的每分钟转数 (rpm):
(a) RPM=31.8 * S/D
1) S = Recommended speed in feet per minute or how fast to move the electrode relative to the part and as specified in Table 19 for plating, or in Paragraph 10.D.(3), and Paragraph 10.D.(4), for anodizing.
S = 以英尺/分钟为单位的建议转速或电极相对于零件的移动速度,电镀见表 19,阳极氧化见第 10.D.(3)段和第 10.D.(4)段的规定。
2) D = Diameter (inches)
D = 直径(英寸)
NOTE: A similar calculation can be made with metric units where S = Electrode speed (meters/minute) and D = Diameter (centimeters).
注: 用公制单位也可进行类似计算,其中 S = 电极速度(米/分),D = 直径(厘米)。
(2) Electrode Size – It is sometimes convenient to know the size of the electrode which will make each job most economical. To calculate this, it is necessary to know the maximum output of the rectifier measured in amperes and the average current density required for the solution being used measured in amperes per square inch.
电极尺寸 – 有时,了解最经济的电极尺寸会很方便。计算时,需要知道整流器的最大输出功率(以安培为单位)和所用溶液所需的平均电流密度(以安培/平方英寸为单位)。
(a) Electrode Size = (Rectifier output) / (Average current density)
电极尺寸 = (整流器输出)/ (平均电流密度)
1) The rectifier output can be taken from the specification tag on the rectifier.
整流器的输出可从整流器上的规格标签中获取。
2) For the required current density, see Table 19 for plating or Paragraph 10.D., for anodizing.
所需的电流密度,电镀见表 19,阳极氧化见第 10.D 段。
NOTE: A similar calculation can be made with metric units.
注: 可使用公制单位进行类似计算。
(3) To calculate ampere-hours for plating, the following formula may be used:
计算电镀所需的安培小时,可使用以下公式:
(a) Ampere-hours = (Area) * (Thickness) * (Plating factor)
安培小时 = (面积)* (厚度)* (电镀系数)
NOTE: Some manufacturers provide plating factors divided by a factor of 10,000; (for example, 0.0250 vs 250).
有些制造商提供的电镀系数除以 10,000 的系数;(例如,0.0250 vs 250)。
1) Area is measured in square inches. This can be calculated from standard formulas for such calculations. Refer to Figure 1.
面积以平方英寸为单位。可根据标准计算公式进行计算。参见图 1。
2) Thickness is the required deposit thickness in inches.
厚度是所需的沉积厚度,单位为英寸。
3) With American units, the plating factor is the number of ampere-hours needed to deposit a volume of 1 cubic inch of metal on the substrate, assuming 100 percent efficiency. The plating factor is supplied by the manufacturer of the solution. Plating factors for solutions listed in this specification are found in Table 19. Similar calculations can be made with metric units and the corresponding plating factor.
使用美式单位时,电镀系数是指在基底上沉积 1 立方英寸金属体积所需的安培小时数,假设效率为 100%。电镀系数由溶液制造商提供。本规范所列溶液的电镀系数见表 19。可使用公制单位和相应的电镀系数进行类似计算。

E. Electrode Preparation
电极制备
(1) Graphite, platinum, platinum-iridium, platinized titanium, or platinized niobium electrodes that specified in Paragraph 4.A., may be used with all acid and alkaline solutions.
第 4.A 段规定的石墨、铂、铂铱、铂化钛或铂化铌电极可用于所有酸性和碱性溶液。
(2) Stainless steel electrodes (Paragraph 4.A.(1)(a) may be used with alkaline solutions, but only in reverse current with acid solutions.
不锈钢电极(第 4.A.(1)(a)段)可用于碱性溶液,但只能以反向电流用于酸性溶液。
(3) Only graphite anodes specified in Paragraph 4.A.(1)(c), may be used with Sifco Process AeroNikl 250 (Paragraph 3.B.(5)(k)), Sifco Process AeroNikl 400 (Paragraph 3.B.(5)(l)), or Sifco Process AeroNikl 575 (Paragraph 3.B.(5)(m)).
只有第 4.A.(1)(c)段规定的石墨阳极可与 Sifco Process AeroNikl 250(第 3.B.(5)(k)段)、Sifco Process AeroNikl 400(第 3.B.(5)(l)段)或 Sifco Process AeroNikl 575(第 3.B.(5)(m)段)一起使用。
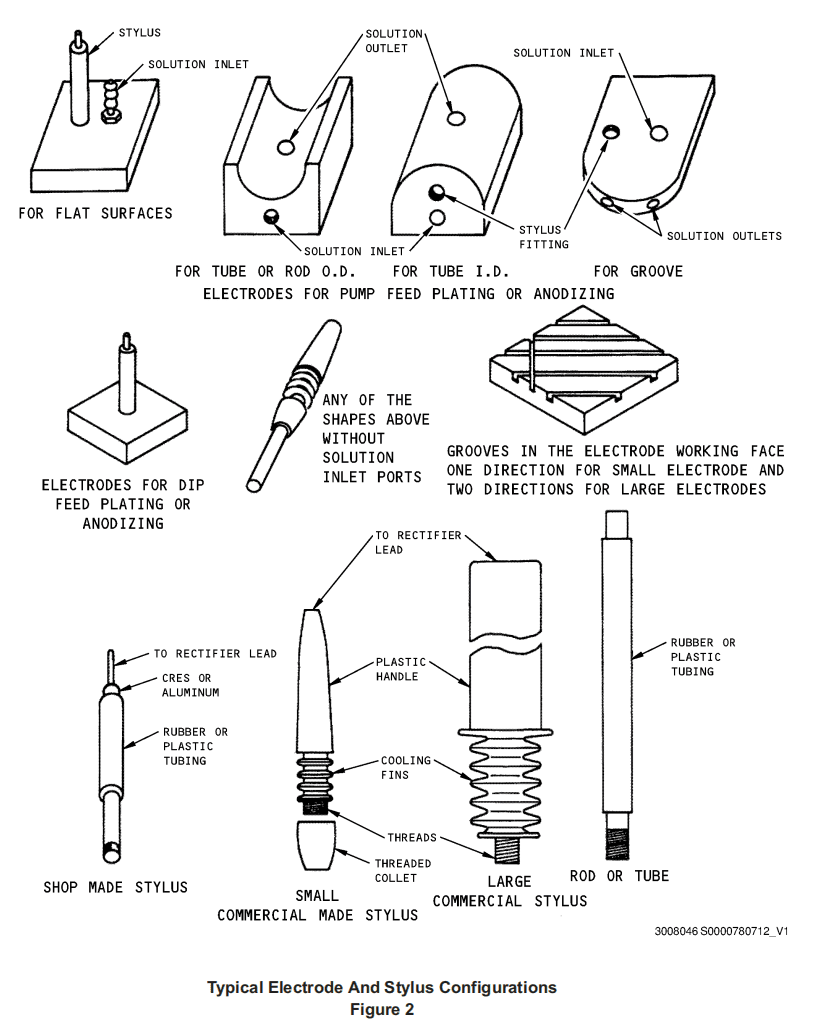
(4) Whenever possible, electrodes must be chosen which conform to the geometry of the work piece so that cleaning, etching, activating and plating are uniform. Several representative graphite electrode configurations are shown in Figure 2.
必须尽可能选择符合工件几何形状的电极,以便清洁、蚀刻、活化和电镀均匀一致。图 2 显示了几种有代表性的石墨电极配置。
(5) To facilitate the flow of gases away from the graphite electrode and the flow of solution to the electrode surface in pump fed plating refer to Paragraph 10.C.(6), cut grooves nominal 1/16 (1.6 mm) inch wide and from 1/8 to 1/4 inch (3 to 6 mm) deep across the electrode work face as shown in Figure 2.
如图 2 所示,为便于气体从石墨电极流出和溶液流向电镀的电极表面(参见第 10.C.(6)段),在电极工作面上开 1/16 英寸(1.6 毫米)宽、1/8 至 1/4 英寸(3 至 6 毫米)深的沟槽。
NOTE: The most economical electrode size can be calculated as shown in Paragraph 9.D.(2).
注: 最经济的电极尺寸可按第9.D.(2)段计算。
(6) Cover materials (Paragraph 3.J.(1)) for the electrodes must be cotton, Dacron (Sifco PermaWrap), polyester, polypropylene, or Scotch-Brite. The contact surface must be covered with enough excess material to allow an overlapping wrap. Secure covers with rubber bands, polyester string ties, tape or by sewing, as illustrated in Figure 3.
电极的覆盖材料(第 3.J.(1)段)必须是棉、Dacron(Sifco PermaWrap)、聚酯、聚丙烯或 Scotch-Brite。接触表面必须覆盖足够多的多余材料,以便重叠包裹。如图 3 所示,用橡皮筋、聚酯扎带、胶带或缝线固定包覆层。
(7) Electrical contacts between the electrode and the power supply must be made by drilling and threading a hole in the electrode and attaching a stylus (Paragraph 4.A.(2)). Either the commercial type or a custom (shop aid) fabricated stylus is satisfactory. Styluses of both types are shown in Figure 2. The stylus must be removed after each use and washed thoroughly. Never interchange electrodes from one solution to another or from a reverse current application to a forward current application. A separate electrode is required for each solution used.
必须在电极上钻孔并穿线,然后装上触针(第 4.A.(2)段),以实现电极与电源之间的电接触。商用触针或定制(车间辅助)触针均可。两种类型的触针如图 2 所示。每次使用后必须取下触针并彻底清洗。切勿将电极从一种溶液换到另一种溶液,或从反向电流应用换到正向电流应用。每种溶液都需要一个单独的电极。
NOTE: Where the application permits (for example, plating or anodizing a small inner diameter), a rotary tool may be used to turn the electrode; and similarly (for example, plating or anodizing an outer diameter), a lathe or turning head may be used to turn the part.
注: 在应用允许的情况下(例如,电镀或阳极氧化小内径),可使用旋转工具转动电极;同样(例如,电镀或阳极氧化外径),可使用车床或车削头转动零件。
F. General Organization And Setup For Hand Held Electrodes
手持电极的通用组织和设置
(1) Set up the solutions, electrodes, rectifier and any other aids in the immediate area where the plating is to be accomplished. Tubes, rods, shells and other round parts must be mounted on a variable speed turning head so that rotation speed and plating thickness uniformity can be controlled. Refer to Paragraph 9.D.(1) for calculation of rotational speed.
将溶液、电极、整流器和其他辅助设备放置在需要电镀的附近区域。管道、棒、壳和其他圆形零件必须安装在变速旋转头上,以便控制旋转速度和电镀厚度的均匀性。有关旋转速度的计算,请参见第 9.D.(1)段。
(2) Avoid cross contamination of cleaning, activating, or plating solutions. Discard any solution contaminated by a different solution, and replace it with fresh solution in a clean container.
避免清洗、活化或电镀溶液的交叉污染。报废任何被不同溶液污染的溶液,并用干净容器中的新鲜溶液替换。
NOTE: For brush processing operations, it is helpful to arrange solution containers in a manner that will preclude the inadvertent cross contamination of cleaning, activating, or processing solutions during the movement of soaked electrodes between solution containers and the surface to be plated or anodized.
注: 对于电刷加工操作,在溶液容器与待电镀或阳极氧化表面之间移动浸湿的电极时,最好将溶液容器摆放整齐,以防止清洗、活化或加工溶液无意中交叉污染。
(3) Prepare a proper size container for each solution to be used.
为使用的每种溶液准备适当大小的容器。
(4) Clearly label each container with the name of the solution to be placed in the container.
在每个容器上清楚标明要放入的溶液名称。
(5) Place sufficient solution in each container to assure that the contact area of the electrode cover will become completely immersed.
在每个容器中放入足够的溶液,以确保电极盖的接触区域完全浸入。
(6) Mark each electrode with the appropriate solution name and polarity to be used.
在每个电极上标明所用溶液的名称和极性。
(7) Place the appropriate electrode into its solution to soak for at least 2 minutes prior to starting any operations.
在开始任何操作前,将适当的电极放入溶液中浸泡至少 2 分钟。
(8) When a forward-current and a reverse-current operation with the same solution is required, use two separate electrodes, solutions, and containers. Avoid any contamination of a forward- or reverse-current solution by the other.
如需使用同一溶液进行正向电流和反向电流操作,应使用两个不同的电极、溶液和容器。避免正向电流溶液或反向电流溶液受到另一种溶液的污染。
(9) Set out enough clean dry wiper material (Paragraph 3.K.(4)) and clean water to perform a complete rinse and wipe dry operation.
列出足够的干净抹布(第 3.K.(4)段)和清水,以便进行全面的沖洗和擦干操作。
(10) Maintain plating solution temperature as specified in Table 19. Never process parts when the temperature of the part or the environment is below 40 F (4 C).
保持电镀溶液温度在表 19 所规定的水平。切勿在零件或环境温度低于 40 °F (4 C) 时加工零件。
NOTE: Prevent arcing of parts. Part scrapping is a potential consequence if arcing occurs.
注: 防止零件起弧。如果发生电弧,零件可能报废。
(11) Make electrical connections secure before application of power. Avoid accidental contact of uncovered electrode areas with the work. Turn off the power before removing the electrical connections. Mark and report any areas where arcing occurred at final inspection. 在通电前确保电气连接牢固。避免未遮盖的电极区域与工作区域意外接触。在拆除电气连接之前应关闭电源。在最终检查时标记并报告发生电弧的任何区域。

10. APPLICATION PROCEDURE 施工应用程序
A. References
参考资料

B. Preparation of Work
准备工作
(1) Work Selection
工作选择
(a) New Manufacture – Area to be worked must be divided into areas which fit the equipment (electrode size and rectifier, refer to Paragraph 9.E.) and can be worked easily. Make sure each area sufficiently overlaps the one adjacent so that, when completed, there will be no missed area and a minimum of overlap area.
新制造-加工区域必须划分为适合设备的区域(电极尺寸和整流器,参见第9.E段)而且可以很容易地加工。确保每个区域与相邻的区域充分重叠,这样,当完成后,就不会有遗漏的区域和最小的重叠区域。
(b) Rework – Plan the work so that the entire damaged area can be plated or anodized at one time. If the area is too large to handle at one time, plan the break up of the area so that each smaller area will require roughly the same number of ampere-hours. Overlapping of areas must still be accomplished so that no areas are missed.
返修–制定工作计划时,应使整个受损区域都能一次性电镀或阳极氧化。如果区域过大,无法一次完成,则应计划分割区域,使每个较小区域所需的安培小时数大致相同。但仍须实现区域重叠,以免遗漏任何区域。
(2) Preliminary Cleaning
初步清洗
(a) If required, remove grease, oil and oily soils from the entire area to be plated or anodized by solvent cleaning or manual cleaning as specified in SOPM 20-30-03.
如有需要,按照 SOPM 20-30-03 的规定,通过溶剂清洗或手工清洗,清除整个电镀或阳极氧化区域的油脂、油和油污。
NOTE: Other techniques may be used as appropriate.
注: 可酌情使用其他技术。
(b) If required, remove scale, rust, etc. from the entire area to be plated or anodized by sanding or brushing as specified in SOPM 20-30-03 or any other applicable method.
如有需要,按 SOPM 20-30-03 规定或任何其他适用方法,用打磨或刷子清除整个电镀或阳极氧化区域的水垢、铁锈等。
(c) File, chip, or sand rough metal areas which can catch and tear the electrode covering.
对可能卡住和撕裂电极覆盖层的粗糙金属区域进行锉磨、切削或打磨。
(d) For rework, feather the damaged area into the undamaged area by filing or sanding. Make the feathered slope as long as possible.
对于返工,通过锉削或打磨将损坏区域羽化到未损坏区域。羽化的斜坡要尽可能长。
(e) Remove loose material created by this step by solvent wiping as specified in SOPM 20-30-03
按照 SOPM 20-30-03 的规定,用溶剂擦拭,清除此步骤产生的松散材料。
(3) Masking
遮蔽
(a) Mask areas selected in Paragraph 10.B.(1) with a masking material (Paragraph 3.I.). Mask rework area so that approximately 1/8 inch (3 mm) border is left exposed around the damaged area.
用遮蔽材料遮蔽第 10.B.(1)段中选定的区域(第 3.I.段)。遮蔽返工区域,使受损区域周围露出约 1/8 英寸(3 毫米)的边框。
(b) To reduce edge buildup or edge burning, use metallic tape (1/8 inch or 3 mm minimum) as the edge maskant around the area to be reworked. The tape must be electrically connected to the work either through a conductive adhesive or by turning an edge of the tape under so that it is in contact with the substrate.
为减少边缘堆积或边缘烧焦,使用金属带(最小 1/8 英寸或 3 毫米)作为待返工区域周围的边缘遮蔽剂。胶带必须通过导电胶或将胶带边缘转到下方使其与基体接触,从而与工件电气连接。
(c) All areas not to be treated and all faying or overlapping surfaces must be protected from contact with these solutions. If metallic tape is to be used, hand clean area to be masked and anodized as specified in SOPM 20-30-03 prior to masking.
所有未处理的区域和所有接合或重叠的表面都必须加以保护,防止与这些溶液接触。如果要使用金属胶带,在遮蔽之前,应按照 SOPM 20-30-03 的规定用手清洁要遮蔽和阳极氧化的区域。
C. Electroplating
电镀
NOTE: Make sure that you use the current revision of the Solution Manufacturer Instructional Manual (I-Manual) or Technical Data Sheet (TDS).
注意: 确保使用最新版本的溶液制造商说明手册 (I-Manual) 或技术数据表 (TDS)。
(1) Prior to plating the final coating (that is, Nickel, Cadmium, Zinc-Nickel) and when a preplate is required, its thickness of approximately 0.00005 inch (1.25 micron, um) should be used and its amp-hr calculated before starting.
在电镀最终镀层(即镍、镉、锌镍)之前,以及需要预镀层时,应使用其厚度约为 0.00005 英寸(1.25 微米,um)的预镀层,并在开始前计算其安培小时数。
(2) The units of factors or plating factors for plating solutions (Cadmium, Nickel, Zinc-Nickel, etc.) are in amp-hr/cubic inches (amp-hr/cubic centimeters).
电镀溶液(镉、镍、锌镍等)的系数或电镀系数的单位是安培小时/立方英寸(安培小时/立方厘米)。
(3) The units of factors plating factors for non-plating solutions (that is, etching, deoxidizing, electrocleaning) are in amp-hr/square inches (amp-hr/square centimeters).
非电镀溶液(即蚀刻、脱氧、电解清洗)的系数电镀系数单位为安时/平方英寸(安时/平方厘米)。
(4) Preplate Preparation
镀前准备
(a) After preparing the part surface as specified in Paragraph 10.B., continue with one of the following:
按照第 10.B 段的规定制备零件表面后,继续进行以下步骤之一:
NOTE: Hydroblast activation is required for titanium unless dry abrasive blasting is used. It is optional for all other substrates.
注: 除非使用干喷砂,否则钛必须进行水喷砂活化。对于所有其他基材,则为可选项。
1) Hydroblast Activation
喷水活化
a) Hydroblast the area to be plated using a slurry of 180-240 grit aluminum oxide (Paragraph 3.K.(1)) and water until a uniform color is obtained. Use an air pressure of 50-115 psi (345-793 kPa), an air-water gun, and a 1-15 gal (4-57 L) paint pressure pot fitted with a stirrer.
使用含 180-240 粒氧化铝(第 3.K.(1)段)和水的浆料对要电镀的区域进行喷砂,直至获得均匀的颜色。使用 50-115 psi (345-793 kPa) 的气压、气水枪和装有搅拌器的 1-15 加仑 (4-57 L) 油漆压力罐。
NOTE: Optional for cadmium on high-strength steel only: use a wiper, wet sand with 180-240 grit aluminum oxide and Sifco Process Solution Cadmium LHE, 5070 (Paragraph 3.B.(1)(e)).
注: 仅适用于高强度钢上的镉涂层:使用抹布,用 180-240 粗细度的氧化铝和 Sifco Process Solution Cadmium LHE, 5070(第 3.B.(1)(e)段)进行湿打磨。
b) Flush off all grit with water and start plating within 1 minute.
用清水冲洗掉所有砂粒,并在 1 分钟内开始电镀。
2) Abrasive blasting (optional)
喷砂(可选)
a) Dry abrasive blasting as specified in SOPM 20-30-03 may be used on titanium instead of hydroblast activation (Paragraph 10.C.(4)(a)1)) if the blast unit is cleaned out and recharged with new grit, the part is blasted using 180-240 grit aluminum oxide with an air pressure of 50-115 psi, the part is blown clean with air, and plating is started within 1 minute.
SOPM 20-30-03 规定的干式喷砂可用于钛,而不是水力喷砂活化(第 10.C.(4)(a)1)段),条件是喷砂装置清理干净并重新装入新砂,使用 180-240 粒氧化铝喷砂,气压为 50-115 psi,用空气将零件吹干净,并在 1 分钟内开始电镀。
3) Chemical Cleaning and Activation
化学清洗和活化
a) Use solutions, operating parameters, and process flow as shown in Table 18.
使用表 18 所示的溶液、操作参数和工艺流程。
b) Do not use solutions from more than one manufacturer during the process.
在工艺过程中,不要使用一个以上制造商生产的溶液。
NOTE: Once a step has started, the best practice is to use that solution to complete the step.
注: 一旦某个步骤开始,最佳做法是使用该溶液完成该步骤。
c) Set the polarity switch in the proper position.
将极性开关置于适当位置。
d) Set the rectifier open-line voltage to approximately the mid-point of the range as shown in Table 18.
将整流器的开线电压调至表 18 所示范围的中点左右。
e) Wet the surface with the proper solution prior to the application of power.
通电前用适当的溶液润湿表面。
f) Turn on the power and place the solution-soaked electrode onto the area to be cleaned and move it back and forth across the part at a speed of 30-50 ft/min (9-15 m/min). Make passes over the part, keeping the electrode and the part wet with the solution.
接通电源,将溶液浸湿的电极放到要清洗的区域,以 30-50 英尺/分钟(9-15 米/分钟)的速度在零件上来回移动。在零件上来回移动,保持电极和零件都被溶液浸湿。
g) Immediately after each solution application, rinse the area with water, unless otherwise noted, but do not allow the part to dry
每次使用溶液后,除非另有说明,应立即用水冲洗该区域,但不要让零件变干


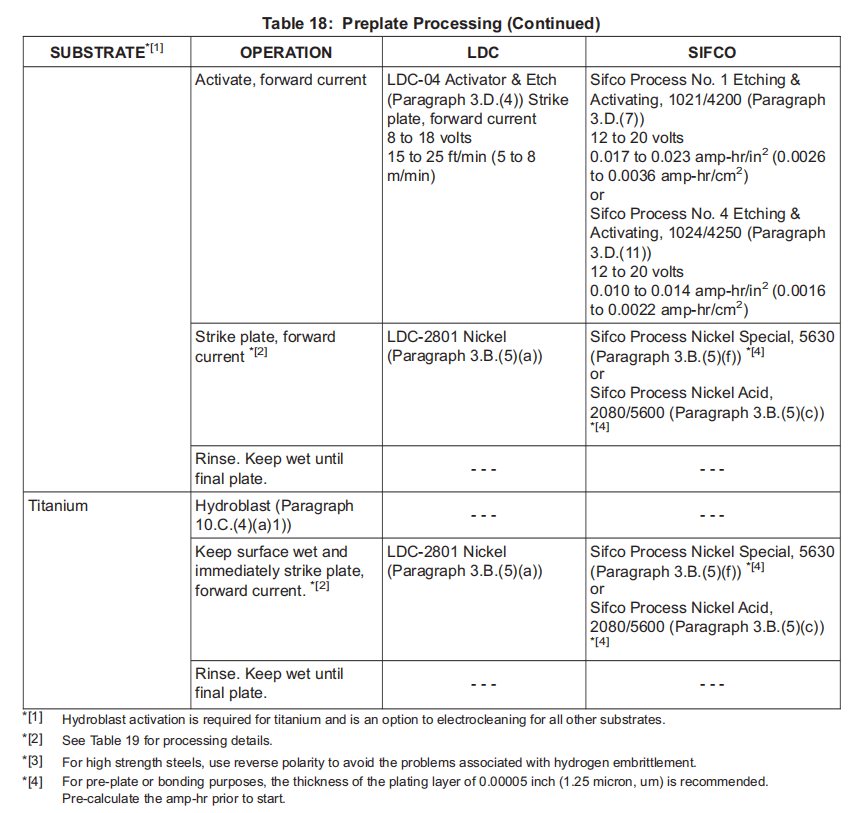
(5) Dip Feed Plating (Hand Held Electrodes)
浸入式电镀(手持电极)
NOTE: For plating parameters refer to Table 19.
注: 电镀参数参见表 19。
NOTE: The solution can be used more than once during an application.
注: 在一次应用中,溶液可多次使用。
(a) Begin with the starting voltage and low speed, then increase the voltage until the plating starts to “burn” at the edges.
从起始电压和低速开始,然后增加电压,直到电镀边缘开始 “烧焦”。
(b) Lower the voltage 0.5-1 volt and continue plating. Refer to Typical Electrode Movements Figure 4 for typical anode movement.
降低电压 0.5-1 伏,继续电镀。有关阳极的典型运动,请参阅图 4 中的典型电极运动。
(c) When burning occurs at the starting voltage specified, slowly increase the anode-to-cathode speed until burning is eliminated. Continue plating at this speed.
当在规定的起始电压下出现烧蚀时,缓慢提高阳极到阴极的速度,直到烧蚀消除。按此速度继续电镀。
(d) Keep the anode and the area being plated wet with solution by repeated dipping of the anode or by using a squeeze bottle.
通过反复浸渍阳极或使用挤压瓶,使阳极和电镀区域保持溶液湿润。
(e) Plate without stopping for the calculated number of ampere-hours.
在计算出的安培小时数内不停电镀。
(f) If plating is interrupted for 30 seconds or less, flood the area with solution (or water) and do not allow the area to dry, then resume plating.
如果电镀中断 30 秒或更短时间,用溶液(或水)浸没该区域,不要让该区域变干,然后继续电镀。
(g) If the area becomes dry or if plating interruption is longer than 30 seconds, reactivate by going back to Paragraph 10.C.(4) and treat the part as if it is made of the plated material (for example, a nickel plated steel part must be activated as if it is a nickel part).
如果电镀区变干或电镀中断时间超过 30 秒,则应返回第 10.C.(4)段重新激活,并将零件视作由电镀材料制成(例如,镀镍钢零件必须视作镀镍零件激活)。



(6) Pump Feed Electrode Plating
泵送电极电镀
NOTE: Pump feed is better than dip feed when thick plating is required (greater than or equal to 0.001 inch or 25 micrometers).
注: 需要厚电镀时(大于或等于 0.001 英寸或 25 微米),泵送比浸渍送效果好。
(a) Start rotation of part or electrode at calculated speed as specified in Paragraph 9.D.(1).
以第 9.D.(1)段规定的计算速度开始旋转零件或电极。
(b) Start pumping solution. Make sure that solution temperature is within the range specified by Table 19.
开始泵送溶液。确保溶液温度在表 19 规定的范围内。
(c) Start plating using the conditions as shown in Table 19. If required, adjust the voltage, the rotational speed, or the solution flow to maintain the current density without burning.
按表 19 所示条件开始电镀。如有需要,可调节电压、转速或溶液流量,以保持电流密度而不烧焦。
(d) If thick plating results in rough, nodular deposits, perform following steps:
如果厚电镀导致粗糙的结节状沉积,请执行以下步骤:
1) Stop plating and remove the roughness by sanding, grinding or filing to restore the smoothness to the surface.
停止电镀,用打磨、研磨或锉刀去除粗糙,使表面恢复光滑。
2) Clean and reactivate the surface as specified in Paragraph 10.C.(4) and treat the part as if it is made of the plated material (for example, a nickel plated steel part must be activated as if it is a nickel part).
按照第 10.C.(4)段的规定清洁和重新激活表面,并将零件视作电镀材料制成(例如,镀镍钢零件必须视作镍零件激活)。
3) Continue plating (and remove roughness when required) until reaching the required thickness.
继续电镀(必要时去除粗糙度),直至达到要求的厚度。
(e) Measure plating thickness with appropriate instrumentation.
用适当的仪器测量电镀厚度。
(f) Store the used solution in a bottle Paragraph 4.A.(3)(a) that is clearly labeled with the solution name, the preparation date, and the amp-hours/L used.
将用过的溶液储存在第 4.A.(3)(a)段的瓶子中,瓶子上要清楚标明溶液名称、配制日期和所用安培-小时/升。
NOTE: Recirculated plating solution may be used for more than one plating job provided the solution is not spent as specified in Paragraph 8.
注: 循环电镀溶液可用于一次以上的电镀作业,但溶液不得按第 8 段的规定使用。
(7) Chromate Treatment for Cadmium, Zinc, and Zinc-nickel
镉、锌和锌-镍的铬酸盐处理
(a) When a chromate conversion coating is required on cadmium, zinc, or zinc-nickel, if possible keep the part wet and apply the coating immediately after the rinse following plating. Flood the surface by immersing, swabbing, or squirting on the solution. If practical, rock the part to minimize contrasting color spots. After applying the coating, rinse and allow to air dry. Do not wipe or rub dry.
如需对镉、锌或锌镍进行铬酸盐转化镀层处理,应尽可能保持零件湿润,并在电镀后的冲洗后立即进行镀层处理。通过浸泡、拭擦或喷洒溶液的方式使表面充水。在可行的情况下,摇晃零件以尽量减少对比色斑点。涂抹涂层后,冲洗并晾干。切勿擦拭或搓干。
CAUTION:DO NOT TOUCH THE TREATED SURFACE BEFORE IT IS FULLY DRY. IF YOU DO NOT OBEY, DAMAGE TO THE COATING CAN OCCUR.
注意:在处理过的表面完全干燥之前,请勿触摸。否则会损坏涂层。
(b) If a delay occurs before applying the chromate conversion coating, perform following steps:
如果在涂刷铬酸盐转化涂层前出现延迟,请执行以下步骤:
1) Dry the plated surface and protect it from contamination.
擦干电镀表面,防止污染。
2) Prior to applying the coating, alkaline clean the dried plating by hand washing the area with a cleaner as specified in SOPM 20-30-03, rinse with clean water and check for water breaks.
在涂镀层之前,用 SOPM 20-30-03 规定的清洁剂手洗已干燥的电镀区域,用清水冲洗并检查是否有断水现象。
3) Reclean if the surface is not water-break-free. Do not allow the surface to dry before applying the coating.
如果表面无断水,则重新清洗。涂装前不要让表面干燥。
(c) The following are intended for either cadmium or zinc:
以下适用于镉或锌:
NOTE: Any other chromate treatment solution which meets the Type II requirements of AMS-QQ-P-416 can also be used.
注: 符合 AMS-QQ-P-416 二类要求的任何其他铬酸盐处理溶液也可使用。
1) Iridite 80 (Paragraph 11.C.(2)) for 5-30 seconds.
Iridite 80(第 11.C.(2)段)5-30 秒。
2) Iridite 8P (Paragraph 11.C.(3)) for 5-30 seconds.
Iridite 8P(第 11.C.(3)段)5-30 秒。
3) Sifco Process Dichromate Conversion Coating, 1720 (Paragraph 3.G.(7)). Apply as received at 60-80°F (16-27°C) for 3-5 seconds.
Sifco 工艺重铬酸盐转化涂层 1720(第 3.G.(7)段)。在 60-80°F (16-27°C) 温度下,按收到时的状态涂抹 3-5 秒钟。
NOTE: Longer immersion or contact times will produce a darker color. An application may be repeated if required.
注: 浸泡或接触时间越长,颜色越深。如有需要,可重复涂抹。
4) Sifco Process Chromate Conversion Coating, 5005 (Paragraph 3.G.(8)). Apply for 30 seconds to 2 minutes.
Sifco 工序铬酸盐转化涂层 5005(第 3.G.(8)段)。涂抹 30 秒至 2 分钟。
5) Sodium dichromate-sulfuric acid solution (Paragraph 11.C.(1)) for 5-10 seconds.
重铬酸钠-硫酸溶液(第 11.C.(1)段),涂抹 5-10 秒。
(d) For zinc-nickel only, apply the following solutions:
仅对锌-镍,使用下列溶液:
1) Sifco Process (Hexavalent) Chromate Conversion Coating, 5030/3004 (Paragraph 3.G.(7)). Apply as received at 100-120°F (38-49°C) for 30-40 seconds.
Sifco Process (Hexavalent) Chromate Conversion Coating, 5030/3004(第 3.G.(7)段)。在 100-120°F (38-49°C)温度下按收到的状态涂抹 30-40 秒。
2) Other manually applicable chromate coatings listed in BAC 5637 or BAC 5680.
BAC 5637 或 BAC 5680 中列出的其他手动应用铬酸盐涂层。
(8) Post-Plate Baking
电镀后烘烤
(a) Unless otherwise specified by the Engineering Drawing, brush plated parts must be baked to the following schedule after plating:
除非工程图另有规定,电镀后必须按以下时间表对刷镀零件进行烘烤:
1) Aluminum parts must be baked at 175-225°F (79-107°C) for 1 hour minimum.
铝质零件必须在 79-107°C (175-225°F) 下烘烤至少 1 小时。
2) Except as allowed by the NOTE in Paragraph 10.C.(8), bake all ferrous alloys within 4 hours following plating as follows:
除第 10.C.(8)段注释允许的情况外,所有铁合金必须在电镀后 4 小时内按以下方法烘烤:
a) Bake parts heat-treated to a strength range of 180 ksi or higher at 350-400°F (177-204°C) for 3 hours minimum.
在 350-400°F (177-204°C)下,对热处理至 180 ksi 或更高强度的零件进行至少 3 小时的烘烤。
b) Bake threaded parts heat-treated to a strength of 160 ksi or higher at 350-400°F (177-204°C) for 3 hours minimum.
螺纹零件在 350-400°F (177-204°C)下热处理至 160 ksi 或更高强度,至少烘烤 3 小时。
c) Bake carburized steel substrates and 440A, B, or C CRES substrates at 250-300°F (121-149°C) for 5-8 hours.
在 121-149°C (250-300°F) 下对渗碳钢基体和 440A、B 或 C CRES 基体进行 5-8 小时的烘烤。
d) Bake Custom 465 CRES heat treated to 220-240 ksi at 350-400°F (177-204°C) for 23 hours minimum. The following ferrous alloys do not require baking after processing:
在 350-400°F (177-204°C)条件下,将热处理至 220-240 ksi 的 Custom 465 CRES 至少烘烤 23 小时。以下铁合金在加工后无需烘烤:
NOTE: The following ferrous alloys do not require baking after processing:
注: 下列铁合金在加工后不需要烘烤:
① Non-threaded parts heat-treated to a strength range below 180 ksi.
非螺纹零件热处理后强度低于 180 ksi。
②Threaded parts heat-treated to a strength range of 150-170 ksi and below.
螺纹零件,热处理后强度范围为 150-170 ksi 及以下。
③ 300 series and A286 corrosion resistant steels.
300 系列和 A286 耐腐蚀钢。
④ Parts heat treated below 220 ksi that have been cadmium plated using LDC-4803 Cadmium S (No Bake), Sifco Process Cadmium (No Bake) Code 2023, Sifco Process Solution Cadmium LHE, 5070, or zinc-nickel plated using Sifco Process Zinc-Nickel LHE, 4018/5970.
使用 LDC-4803 Cadmium S (No Bake)、Sifco Process Cadmium (No Bake) Code 2023、Sifco Process Solution Cadmium LHE, 5070 或 Sifco Process Zinc-Nickel LHE, 4018/5970 进行电镀的 220 ksi 以下零件。

D. Anodizing of Aluminum
铝阳极氧化
NOTE: The part and/or solution may need cooling or heating to meet the temperature requirements for the anodizing solutions.
注: 零件和/或溶液可能需要冷却或加热,以达到阳极氧化溶液的温度要求。
(1) Painting Sealed Anodized Aluminum
给密封阳极氧化铝上漆
CAUTION :KEEP SEALED ANODIZED PARTS CLEAN. IF YOU DO NOT OBEY, IT COULD JEOPARDIZE SUBSEQUENT ORGANIC COATING ADHESION.
注意 :保持密封阳极氧化零件清洁。否则会损害后续有机涂层的附着力。
(a) The application of liquid coating must begin within 72 hours of the completion of the sealed anodize process.
必须在密封阳极氧化工艺完成后 72 小时内开始涂刷液体涂料。
CAUTION :BE CAREFUL WHEN YOU CLEAN SURFACES WITH A WIPE PROCEDURE. IF YOU CLEAN SURFACES TOO MUCH, DAMAGE OF THE ANODIC LAYER AND SUBSEQUENT COATING ADHESION FAILURES CAN OCCUR.
注意 :使用擦拭程序清洁表面时要小心。如果过度清洁表面,可能会损坏阳极层,导致涂层附着失效。
(b) If surface becomes contaminated, it must be cleaned as specified in SOPM 20-30-03. If the contamination is strictly particulate, it must be cleaned with compressed air.
如果表面受到污染,必须按照 SOPM 20-30-03 的规定进行清洁。如果污染完全是微粒,则必须用压缩空气清洁。
(2) Preparation
准备工作
(a) Prepare part surface as specified in Paragraph 10.B.
按第 10.B 段的规定准备零件表面。
(b) Electroclean as specified in Table 18 using forward current with one of the following solutions:
按照表 18 的规定,使用下列溶液之一的正向电流进行电解清洗:
1) Sifco Process Electrocleaning, 1010/4100.
2) LDC-01 Electroclean.
(c) Clean for 3-5 minutes, then rinse and check for water breaks.
清洗 3-5 分钟,然后冲洗并检查是否有断水。
(d) Reclean as required until there are no water breaks. Keep the parts wet with water until anodizing starts.
根据需要重新清洗,直到没有断水为止。在阳极氧化开始之前,要保持零件被水浸湿。
(3) Dip Feed Anodizing
浸入式阳极氧化
(a) Use pump feed anodizing (Paragraph 10.D.(4)) for BSAA, hard anodize, and for color match anodize using chromic acid solution.
使用泵送阳极氧化(第 10.D.(4)段)进行 BSAA、硬质阳极氧化,以及使用铬酸溶液进行配色阳极氧化。
NOTE: An anodizing solution may be used more than once during an application.
注: 阳极氧化溶液可在一次应用中多次使用。
(b) For the anodizing solutions as shown in Table 20, use the manufacturer’s recommended processing parameters of current density, voltage, temperature, and speed. In the absence of such information, use the parameters as shown in Table 20 as guidelines.
对于表 20 所示的阳极氧化溶液,应使用制造商推荐的电流密度、电压、温度和速度等加工参数。如果没有此类信息,则使用表 20 所示参数作为指导。
(c) For all anodizing, maintain a cathode (anodizing electrode) to anode (part) area ratio of 75-100 percent.
在所有阳极氧化过程中,阴极(阳极氧化电极)与阳极(零件)的面积比保持在 75%-100%。
(d) Begin anodizing using the starting voltage and electrode-to-part speed shown.
按照所示的起始电压和电极对零件的速度开始阳极氧化。
(e) Increase the voltage gradually at a rate of 3-4 volts per minute or 1.5-2 volts every 30 seconds until the maximum voltage is achieved or until the required amp-hr is reached.
以每分钟 3-4 伏或每 30 秒 1.5-2 伏的速度逐渐增加电压,直至达到最大电压或所需的安培小时数。
CAUTION :DO NOT CHANGE THE ELECTRODE DIRECTION ON THE ANODIZED AREA. IF YOU DO NOT OBEY, IT CAN CAUSE UNEVEN DEPOSIT THICKNESS
注意 :不要改变阳极氧化区的电极方向。如果不遵守,会导致镀层厚度不均匀。
(f) Use a back and forth, or a circular motion of the electrode. Avoid changes in direction of the electrode on the area being anodized. Change direction only when the electrode is over the mask and completely clear of the anodize area as illustrated in Figure 4. Use consistent and uniform electrode movement to ensure even distribution of the coating.
电极应来回移动或做环形运动。避免在阳极氧化区域上改变电极方向。如图 4 所示,只有当电极越过遮蔽物并完全离开阳极氧化区域时才可改变方向。电极移动要一致、均匀,以确保涂层分布均匀。
(g) A combination of electrode movement and voltage range control will ensure that the proper current is maintained throughout the process.
将电极移动和电压范围控制相结合,可确保在整个过程中保持适当的电流。
(h) Keep the electrode and area being anodized wet with solution by repeated dipping of the electrode or by using a squeeze bottle to deliver solution to the electrode pad and area. If anodizing is interrupted, flood the area with water and do not allow the part to dry. Resume anodizing without reactivation.
通过反复浸渍电极或使用挤压瓶向电极和阳极氧化区域输送溶液,使电极和阳极氧化区域保持溶液湿润。如果阳极氧化中断,则用水淹没该区域,不要让零件干燥。在不重新激活的情况下恢复阳极氧化。
(i) When the maximum voltage is reached, anodize until the calculated ampere-hour or anodize time is achieved.
达到最大电压后,进行阳极氧化,直至达到计算的安培小时或阳极氧化时间。
(j) Discard the solution after each application.
每次使用后都要报废溶液。
(k) Rinse the surface. Do not allow the part to dry before sealing.
冲洗表面。密封前不要让零件干燥。
(4) Pump Feed Anodizing
泵送阳极氧化
NOTE: It is suggested that this method be used for all types of anodizing, especially when the anodize solution requires heating or cooling.
注: 建议所有类型的阳极氧化都采用这种方法,特别是当阳极氧化溶液需要加热或冷却时。
(a) Use pump feed anodizing for boric-sulfuric acid anodize (BSAA), hard anodize, and for color match anodize using chromic acid solution.
对于硼硫酸阳极氧化 (BSAA)、硬质阳极氧化以及使用铬酸溶液的配色阳极氧化,应使用泵进料阳极氧化。
(b) Start rotation of equipment and start pumping the solution through the heater or cooler as required to deliver the solution at the recommended temperature.
开始转动设备,并根据需要通过加热器或冷却器泵送溶液,使溶液达到建议温度。
(c) Start anodizing at zero voltage.
在零电压下开始阳极氧化。
(d) Increase the voltage gradually at a rate of 3-4 volts per minute or 1.5-2 volts per 30 seconds or as noted below in step Paragraph 10.D.(4)(e).
以每分钟 3-4 伏或每 30 秒 1.5-2 伏的速度,或按照下文第 10.D.(4)(e)段所述步骤,逐渐增加电压。
(e) Perform following steps:
执行以下步骤:
1) For chromic and sulfuric acid anodizing:
铬酸和硫酸阳极氧化:
a) Slowly increase the voltage from zero to the recommended operating range at a rate of 3-4 volts per minute or 1.5-2 volts per 30 seconds.
以每分钟 3-4 伏或每 30 秒 1.5-2 伏的速度将电压从零缓慢增加到建议的操作范围。
b) Adjust rotational speed, voltage, and solution flow to stay within the proper range. Maintain a constant voltage as the coating thickness increases.
调整转速、电压和溶液流量,使其保持在适当范围内。随着涂层厚度的增加,保持电压恒定。
c) Continue anodizing for a minimum of 0.02 amp-hr/in2 (0.003 amp-hr/ cm2 ) (2000 series alloys require 0.03 amp-hr/in2 or 0.005 amp-hr/cm2 ).
继续阳极氧化至少 0.02 amp-hr/in2(0.003 amp-hr/cm2)(2000 系列合金需要 0.03 amp-hr/in2或 0.005 amp-hr/cm2)。
2) For BSAA:
对于 BSAA:
a) Slowly increase the voltage from zero to 22±2 volts at a rate of 3-4 volts per minute or 1.5-2 volts per 30 seconds.
以每分钟 3-4 伏或每 30 秒 1.5-2 伏的速度将电压从零缓慢升至 22±2 伏。
b) Maintain a solution flow rate at 1-1.3 liters (34-44 fl oz) per minute.
溶液流速保持在每分钟 1-1.3 升(34-44 盎司)。
c) Continue anodizing to 0.005-0.009 amp-hr/in2 (0.0008-0.0014 amp-hr/cm2 ) (2000 series requires 0.008-0.011 amp-hr/in2 or 0.0012-0.0017 amp-hr/cm2 ).
继续阳极氧化至 0.005-0.009 amp-hr/in2(0.0008-0.0014 amp-hr/cm2)(2000 系列要求 0.008-0.011 amp-hr/in2或 0.0012-0.0017 amp-hr/cm2)。
CAUTION :DO NOT LIFT MASKING MATERIALS WHEN YOU DO REWORK OF THE HARD ANODIZE COATINGS. IF YOU DO NOT OBEY, CHEMICAL DAMAGE OF THE ADJACENT COATING CAN OCCUR.
注意 :在对硬质阳极氧化涂层进行返工时,请勿揭开遮蔽材料。否则会对相邻涂层造成化学损坏。
3) For hard anodizing:
用于硬质阳极氧化:
NOTE: At 0.5 amp/in2 (0.08 amps/cm2 ) and 50°F (10°C), approximately 0.13 amp-hr/in2 (0.020 amp-hr/cm2 ) will produce an anodized coating 0.002 inch thick (51 micrometers) (2000 series alloys require 0.17 amp-hr/ in2 or 0.026 amp-hr/cm2 ).
注: 在 0.5 安培/平方英寸(0.08 amps/cm2)和 10°C (50°F) 的条件下,大约 0.13 amp-hr/in2(0.020 amp-hr/cm2)将产生 0.002 英寸厚(51 微米)的阳极氧化涂层(2000 系列合金需要 0.17 amp-hr/in2或 0.026 amp-hr/cm2)。
a) Slowly increase the voltage until the calculated amperage level is reached.
缓慢增加电压,直到达到计算的安培数水平。
b) Maintain the amperage by adjusting the voltage as required up to the recommended maximum. Adjust rotational speed and solution flow.
根据需要调节电压以保持安培数,直至达到建议的最大值。调整转速和溶液流量。
c) Continue anodizing until the calculated amp-hr value is reached.
继续阳极氧化,直至达到计算的安培小时值。
(f) If anodizing is interrupted, keep the area wet with water. Resume anodizing without activating.
如果阳极氧化中断,则用水保持该区域湿润。在不激活的情况下继续阳极氧化。
(g) Rinse the surface. Do not allow the part to dry before sealing.
冲洗表面。密封前不要让零件干燥。
(5) Sealing of Anodize Coating
阳极氧化涂层的密封
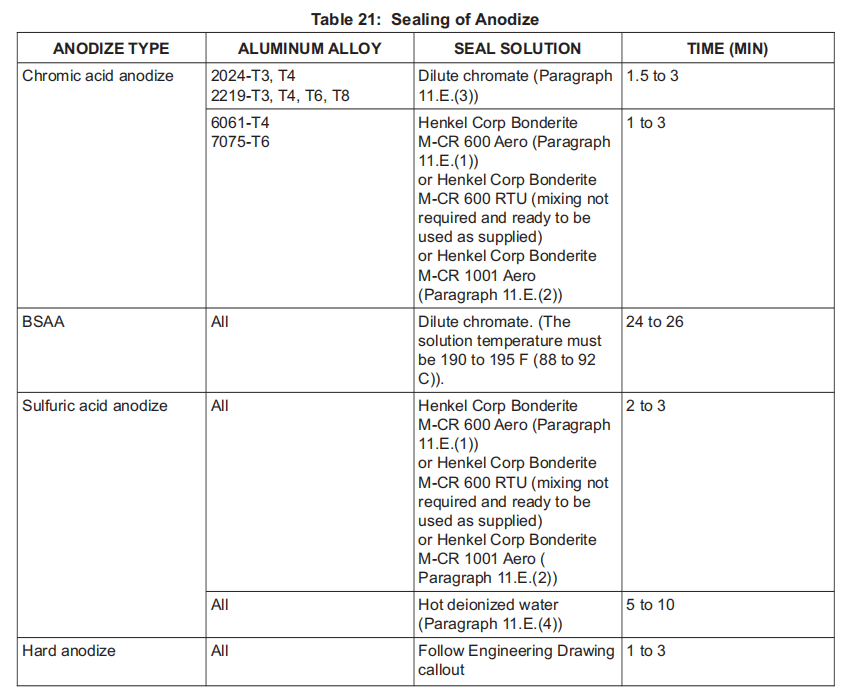
(a) Immerse parts that can be immersed in the sealing solution for the time as shown in Table 21.
将可以浸泡的零件浸入密封溶液中,浸泡时间如表 21 所示。
(b) For parts that cannot be immersed, swab or squirt on room temperature sealing solution.
对于无法浸入的零件,用棉签拭擦或喷洒室温密封溶液。
(c) Keep surface flooded with solution for the time as shown in Table 21.
保持表面浸入溶液的时间如表 21 所示。
(d) Rinse and dry the surface.
冲洗并擦干表面。
(e) If hot deionized water sealing is required, place a generous amount of cotton over the anodized area.
如果需要用热去离子水密封,则在阳极氧化区域放置大量棉花。
(f) Saturate the cotton by pumping or pouring hot deionized water onto the part for the time as shown in Table 21.
在表 21 所示的时间内,用泵将热去离子水抽到或倒到零件上,使棉花饱和。
(6) Rework of Chromic Acid Anodized Surfaces Using Sifco Process Sulfuric Acid Anodizing (Type II), 5011, And Chemical Conversion Seal Solutions
使用 Sifco 工艺硫酸阳极氧化(II 型)、5011 和化学转换密封溶液返修铬酸阳极氧化表面
NOTE: The solution may be used more than once during an application.
注: 溶液可在一次应用中多次使用。
(a) Document rework as required by the applicable quality assurance provisions.
按照适用的质量保证规定,记录返工情况。
(b) Compute the required anodizing current by multiplying the recommended current density value of Sifco Process Sulfuric Acid Anodizing (Type II), 5011, from Table 20 by the area being anodized or the area of the electrode, whichever is smaller.
将表 20 中的 Sifco 工艺硫酸阳极氧化(II 型),5011的建议电流密度值乘以阳极氧化面积或电极面积(以较小者为准),计算所需阳极氧化电流。
(c) Compute the total ampere-hours required to form the anodic layer by multiplying the area to be anodized in square inches by the factor 0.035 amp-hr/in2 (or by multiplying the area in square centimeters by 0.0054 amp-hr/cm2 ).
将以平方英寸为单位的阳极氧化面积乘以系数 0.035 安培-小时/平方英寸 (或以平方厘米为单位的阳极氧化面积乘以 0.0054 安培-小时/平方厘米), 计算形成阳极氧化层所需的总安培小时数。
(d) When using Sifco Process Sulfuric Acid Anodizing (Type II), 5011, anodizing solution to rework damaged chromic acid anodizing on part surfaces, hand clean area with solvent as specified in SOPM 20-30-03, using a wiper (Paragraph 3.K.(4)) until a wipe with a clean wiper yields no residue.
当使用 Sifco Process Sulfuric Acid Anodizing (Type II),5011,阳极氧化溶液对损坏的铬酸阳极氧化零件表面进行返修时,用 SOPM 20-30-03 规定的溶剂手工清洁该区域,并使用抹布(第 3.K.(4)段),直到用干净的抹布擦拭无残留为止。
NOTE: This step is not required if solvent cleaning was done prior to masking.
注: 如果在遮蔽之前进行了溶剂清洁,则不需要此步骤。
1) Change wiper as needed.
根据需要更换擦拭布。
2) Hand clean the area a second time with anodizing solution using a wiper until a wipe with a wet wiper yields no residue.
使用擦拭布用阳极氧化溶液对该区域进行第二次手工清洁,直到用湿擦拭布擦拭无残留为止。
3) Do not allow the work surface to dry, but begin anodizing immediately after cleaning.
不要让工作面干燥,清洁后立即开始阳极氧化。
CAUTION :DO NOT CHANGE THE ELECTRODE DIRECTION ON THE ANODIZED AREA. IF YOU DO NOT OBEY, IT CAN CAUSE UNEVEN DEPOSIT THICKNESS
注意:不要改变阳极氧化区域的电极方向。否则会导致沉积厚度不均匀
(e) Begin anodizing at zero volts and slowly increase the voltage at a rate of 3-4 volts per minute using an electrode to part speed of approximately 10 ft/min (3 m/min).
从零伏开始阳极氧化,然后以每分钟 3-4 伏的速度缓慢增加电压,电极到零件的速度约为 10 英尺/分钟(3 米/分钟)。
1) Hold amperage constant until the required ampere-hour have been achieved. Do not allow the anodizing voltage to rise above 21 volts during processing.
保持安培数不变,直到达到所需的安培小时数。在加工过程中,不要让阳极氧化电压超过 21 伏。
2) Use a back and forth or circular motion of the electrode. Change direction only when the electrode is over the mask and completely clear of the anodize area as illustrated in Figure 4. Use consistent and uniform electrode movement (approximately 10 ft/min or 3 m/min) to ensure even distribution of the coating.
使用电极来回或环形运动。如图 4 所示,只有当电极越过遮蔽物并完全离开阳极氧化区域时才可改变方向。使用一致且均匀的电极运动(约 10 英尺/分钟或 3 米/分钟),以确保涂层均匀分布。
(f) Keep the electrode and area being anodized wet with solution by repeated dipping of the electrode or by using a squeeze bottle to deliver solution to the electrode pad and area. If anodizing is interrupted, flood the area with water and do not allow the part to dry. Resume anodizing without reactivation.
通过反复浸渍电极或使用挤压瓶向电极和区域输送溶液,使电极和阳极氧化区域保持溶液湿润。如果阳极氧化中断,则用水淹没该区域,不要让零件干燥。在不重新激活的情况下恢复阳极氧化。
(g) Rinse the surface. Do not allow the part to dry before sealing.
冲洗表面。密封前不要让零件干燥。
(h) Discard the solution after each application.
每次使用后都要报废溶液。
(i) Seal reworked anodic surfaces using Henkel Corp Chemical Conversion solutions (Bonderite M-CR 600 Aero, Bonderite M-CR 600 RTU Aero, or Bonderite M-CR 1001 Aero solutions).
使用 Henkel Corp 化学转换溶液(Bonderite M-CR 600 Aero、Bonderite M-CR 600 RTU Aero 或 Bonderite M-CR 1001 Aero 溶液)密封阳极表面。
1) Swab or squirt Henkel Corp Bonderite solution at room temperature on the area that was anodized.
在室温下将 Henkel Corp Bonderite 溶液拭擦或喷洒在被阳极氧化的区域。
2) Keep surface flooded with Henkel Corp Bonderite solution for a minimum of 30 seconds.
用 Henkel Corp Bonderite 溶液浸泡表面至少 30 秒钟。
3) Rinse part surfaces and dry as specified in BAC 5719 or SOPM 20-43-03.
按照 BAC 5719 或 SOPM 20-43-03 的规定冲洗零件表面并干燥。
E. Manual Electrochemical Etching
手动电化学蚀刻
NOTE: This procedure may be used on aluminum, corrosion resistant steel, nickel base alloys and steels heat treated to less than 220 ksi to remove smeared metal prior to penetrant inspection.
注: 此程序可用于铝、耐腐蚀钢、镍基合金和热处理至 220 ksi 以下的钢,以在渗透检查前去除脏污金属。
(1) Determination of Etch Factor
确定蚀刻系数
(a) Etch factors vary with specific solution and alloy as shown in Table 22. Determine etch factors not found in Table 22 as follows:
蚀刻系数因具体溶液和合金而异,如表 22 所示。表 22 中没有的蚀刻系数按以下方法确定:
1) Use sheet stock of the same material as the part for making test specimens.
使用与零件相同材料的板材制作测试样本。
2) Clean and mask as specified in Paragraph 10.E.(3) leaving a test area of approximately 2 sq inches (13 cm2 ).
按照第 10.E.(3)段的规定进行清洁和遮蔽,留下约 2 平方英寸(13 平方厘米)的测试区域。
3) Measure the specimen thickness in at least three places.
至少在三处测量试样厚度。
4) Determine the area of the surface to be etched.
确定待蚀刻表面的面积。
5) Electroclean according to Paragraph 10.E.(4).
按照第 10.E.(4)段进行电解清洗。
6) Electrochemically etch as specified in Paragraph 10.E.(5) for 0.30 ampere-hour, minimum.
按照第 10.E.(5)段的规定进行电化学蚀刻,最小蚀刻电流为 0.30 安培-小时。
7) Measure specimen thickness at same locations. Calculate average thickness reduction from all measured locations.
在相同位置测量试样厚度。计算所有测量点的平均厚度减少量。
8) Calculate the etch factor using the following equation. Use American or metric units consistently; do not mix them in the calculation:
使用以下公式计算蚀刻系数。统一使用美制或公制单位,计算时不要混用:
Etch factor = (Ampere-hour) / ((Area) * (Thickness reduction))
蚀刻系数 = (安培小时) / ( (面积) * (厚度缩减))
where:
其中
Ampere-hour = Ampere hours used in Paragraph 10.E.(1)(a)6);
安培小时 = 第 10.E.(1)(a)6)段中使用的安培小时;
Area = Area that was etched in square inches (or cm2 );
面积 = 以平方英寸(或平方厘米)为单位的蚀刻面积;
Thickness reduction = Amount of metal removed in inches (or cm).
减少的厚度 = 以英寸(或厘米)为单位去除的金属量。

(2) Calculations
计算
(a) Calculate the area of the surface to be etched.
计算待蚀刻表面的面积。
(b) Using the etch factor from Paragraph 10.E.(1)(a)8), calculate the required ampere-hours with the following equation:
使用第 10.E.(1)(a)8)段中的蚀刻系数,按以下公式计算所需的安培小时:
Ampere-hours = (Etch factor) * (Area) * (Thickness reduction)
安培小时 = (蚀刻系数) * (面积) * (厚度缩减)
where:
其中:
Etch factor = Etch factor used in Table 22.
蚀刻系数 = 表 22 中使用的蚀刻系数。
Area = Area to be etched (in2 or cm2 )
面积 = 需要蚀刻的面积(平方英寸或平方厘米)
Thickness reduction = Thickness of metal to be removed (in or cm)
厚度缩减 = 要去除的金属厚度(英寸或厘米)
(3) Surface Preparation
表面处理
(a) Prepare part surface as specified in Paragraph 10.B.
按照第 10.B 段的规定制备零件表面。
(b) Use maskant and supplemental protective materials to completely protect all areas that will not be etched from the electrolyte solutions.
使用遮蔽剂和辅助保护材料,完全保护所有不会被电解质溶液蚀刻的区域。
(4) Electrocleaning
电清洗
(a) Apply solutions with a polyethylene squeeze bottle or by dipping the electrode into a pan of the solution. Discard solutions that have been used for dipping.
用聚乙烯挤压瓶或将电极浸入盛有溶液的槽中涂抹溶液。报废浸渍过的溶液。
(b) Wet the electrode and the surface to be cleaned with LDC-01 Electroclean; or Sifco Process Electrocleaning, 1010/4100.
用 LDC-01 Electroclean 或 Sifco Process Electrocleaning, 1010/4100 润湿电极和待清洁表面。
(c) Turn rectifier power on and set open line voltage at 8 volts. Set current switch in forward position except use reverse position for steel alloys susceptible to hydrogen embrittlement.
接通整流器电源,将开路电压设置为 8 伏。将电流开关设置在正向位置,但对于易发生氢脆的钢合金则使用反向位置。
(d) Place the electrode that was wetted in cleaning solution onto the area to be cleaned and move it back and forth as shown in Figure 4 at a speed of 30-50 ft/min (6-10 in/sec, 9-15 m/min, or 15-25 cm/sec). Keep the electrode and part wet with solution.
将在清洗溶液中浸湿的电极放在要清洗的区域上,如图 4 所示,以 30-50 英尺/分钟(6-10 英寸/秒,9-15 米/分钟,或 15-25 厘米/秒)的速度来回移动。保持电极和零件被溶液浸湿。
(e) Clean for approximately 0.020 amp-hr/in2 (0.0031 amp-hr/cm2 ).
清洁约 0.020 安培-小时/平方英寸(0.0031 安培-小时/平方厘米)。
(f) Rinse thoroughly with water. Repeat, as required, until the surface is water-break-free. Keep surface wet until etching Paragraph 10.E.(5) is started.
用清水彻底冲洗。根据需要重复上述步骤,直至表面无断水。在开始第 10.E.(5)段的蚀刻前,应保持表面湿润。
(5) Electrochemical Etching
电化学蚀刻
(a) Wet the electrode and the surface to be cleaned with Sifco Process No. 2 Etching, 1022/4300 or other etching solution as specified in Table 23. Ensure that power is off if the electrode is used to wet the surface.
用 Sifco Process No. 2 Etching, 1022/4300 或表 23 规定的其他蚀刻液润湿电极和待清洁表面。如果使用电极润湿表面,应确保电源关闭。
(b) Set rectifier open line voltage at 10 volts. Set current switch in reverse position.
将整流器开路电压设置为 10 伏。将电流开关设置在反向位置。
(c) Place the electrode that was soaked in etching solution onto the area to be cleaned and move it back and forth as shown in Figure 4 at a speed of 30-50 ft/min (6-10 in/sec, 9-15 m/min, or 15-25 cm/sec).
将浸泡在溶液中的电极放在要清洁的区域上,并以 30-50 英尺/分钟 (6-10 英寸/秒,9-15 米/分钟,或 15-25 厘米/秒)的速度来回移动,如图 4 所示。
NOTE: Use the same solution that was used to wet the surface. Do not mix different solutions.
注: 使用润湿表面的相同溶液。不要混合不同的溶液。
(d) Keep the electrode and part wet with solution. Etch for the ampere-hours calculated in Paragraph 10.E.(2).
保持电极和零件被溶液浸湿。按第 10.E.(2)段计算的安培小时进行蚀刻。
(e) Rinse thoroughly with water immediately after etching. If there is any smut on the surface, clean as follows:
蚀刻后立即用水彻底冲洗。如果表面有污垢,按以下方法清洗:
1) Wet the electrode and the surface to be desmutted with Sifco Process No. 3 Etching & Desmutting, 1023, Sifco Process No. 3 Etching & Desmutting, 4350, or other desmutting solution as specified in Table 23. Ensure that power is off if the electrode is used to wet the surface.
用 Sifco Process No.3 Etching 和 Desmutting, 1023、Sifco Process No.3 Etching 和 Desmutting, 4350 或表 23 规定的其他溶液润湿电极和待除模表面。如果电极用于润湿表面,应确保电源关闭。
2) Electrochemical etch at 18 volts (current switch in reverse position) until the surface color no longer changes.
在 18 伏电压下进行电化学蚀刻(电流开关在反向位置),直至表面颜色不再改变。
NOTE: Use the same solution that was used to wet the surface. Do not mix different solutions.
注: 使用与润湿表面相同的溶液。不要混合不同的溶液。
3) Rinse thoroughly with water immediately after etching.
蚀刻后立即用水彻底冲洗。
(f) Dry the surface.
擦干表面。
(g) Remove masking.
去除遮蔽物。
F. Rework
返工
NOTE: Document rework as required by the applicable quality assurance provisions.
注: 按适用的质量保证规定的要求记录返工情况。
(1) Stripping Brush Plating
去除电镀刷
(a) Strip the protective finishes as specified in SOPM 20-30-02 or Table 23.
按照 SOPM 20-30-02 或表 23 的规定剥离保护层。
NOTE: Ideally, the best stripping technique is to strip only the plating that needs to be replated. Realistically, the stripping solutions will attack the plating and basis metal. Careful masking and minimal stripping time will help reduce the damage to mask edges and basis metal.
注: 理想情况下,最佳的剥离技术是只剥离需要补镀的镀层。实际上,剥离溶液会侵蚀电镀层和基底金属。仔细遮蔽和尽量缩短剥离时间将有助于减少对遮蔽边缘和基底金属的损坏。
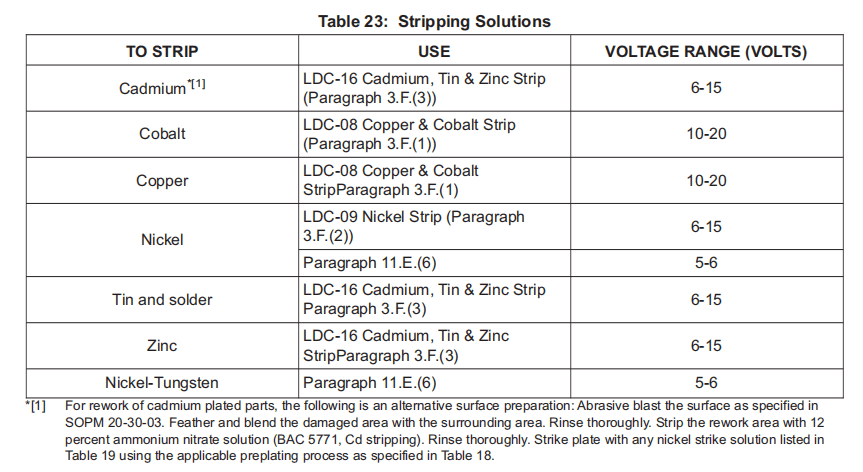
(2) Stripping Brush Anodize
去除刷阳极氧化层
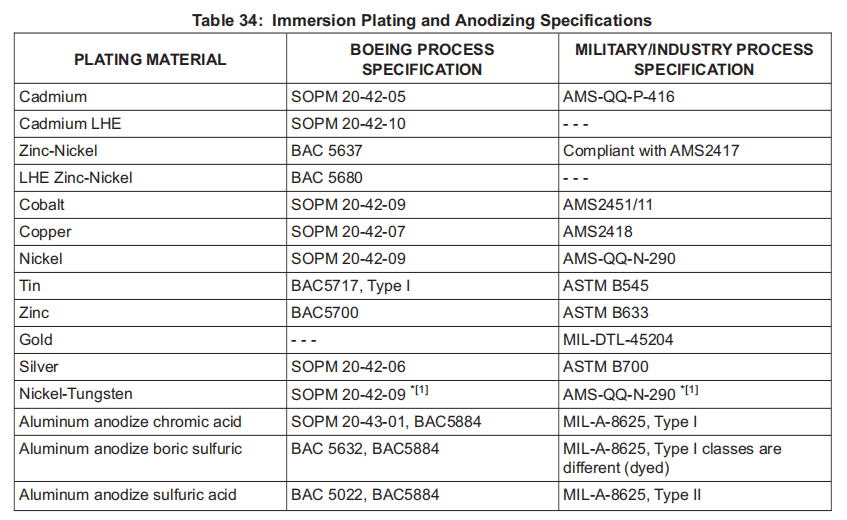
(a) Strip in accordance with the corresponding immersion anodizing specification as shown in Table 34 or strip at the voltage as shown in Table 23 with forward current using one of the following solutions:
按照表 34 所示相应的浸渍阳极氧化规范进行剥离,或使用下列溶液之一,在表 23 所示电压下以正向电流进行剥离:
1) LDC-01 Electroclean.
2) Sifco Process Electrocleaning, 1010/4100.
(b) Rinse thoroughly with water and allow to air dry.
用清水彻底冲洗并干燥。
NOTE: Wiping dry is permitted.
注: 允许擦干。
(c) Use a continuity tester Paragraph 7.B.(4)(c) to check that the stripping is complete over the whole surface. Continue the stripping if necessary.
使用连续性测试仪第 7.B.(4)(c)段检查整个表面的剥离是否完成。必要时继续剥离。
(3) Replating or Re-Anodizing
重新电镀或重新阳极氧化
(a) Following stripping, replate as specified in Paragraph 10.C., or re-anodize as specified in Paragraph 10.D.
剥离后,按第 10.C 段规定进行重新电镀,或按第 10.D 段规定重新阳极氧化。
(4) Color Match Rework on Chromic Acid Anodize with Henkel Corp Bonderite M-CR 1000L Aero Solution
用 Henkel Corp Bonderite M-CR 1000L Aero 溶液进行铬酸阳极氧化的配色返工
(a) Preparation of Work
准备工作
1) Prepare work as specified in Paragraph 10.B.(1)(b) and Paragraph 10.B.(2).
按照第 10.B.(1)(b)段和第 10.B.(2)段的规定准备工作。
2) Blend out surface defects using abrasive paper (Paragraph 3.K.(2)) or a file (Paragraph 3.K.(3)).
用砂纸(第 3.K.(2)段)或锉刀(第 3.K.(3)段)打磨表面缺陷。
3) Mask area surrounding blendout with a tape from Paragraph 3.I. Leave approximately 3/16 inch (5 mm) border of original anodize coating exposed.
用第 3.I 段中的胶带遮盖混合区周围的区域,露出约 3/16 英寸 (5 毫米)的原始阳极氧化涂层边缘。
NOTE: No aluminum tape edge mask required.
注: 无需铝带边缘遮蔽。
4) Examine appearance of blendout area. If area appears shinier than surrounding area, tone down by sanding with sandpaper.
检查混合区域的外观。如果该区域看起来比周围区域更亮,则用砂纸打磨以降低光泽度。
(b) Cleaning and Stripping Before Anodizing on Aluminum
铝阳极氧化前的清洁和剥离
1) Electroclean for 2-5 minutes as specified in Table 18 using forward current with one of the following solutions:
按照表 18 的规定,使用以下溶液之一的正向电流电解清洗 2-5 分钟:
a) Sifco Process Electrocleaning, 1010/4100.
b) LDC-01 Electroclean.
2) Rinse and check for water breaks. Reclean as required until there are no water breaks. Use continuity tester to assure that all anodize coating has been removed.
冲洗并检查是否有断水。根据需要重新清洗,直到没有断水为止。使用连续性测试仪确保所有阳极氧化涂层都已去除。
3) Desmut electroclean area using Sifco Process Sulfuric Acid Anodizing (Type II), 5011.
使用 Sifco Process Sulfuric Acid Anodizing (Type II),5011,对电解清洁区域进行脱膜处理。
4) Rinse the surface.
冲洗表面。
(c) Method for Preparation of Color Chips
制备色片的方法
1) Use nominal 6 inches by 6 inches by 0.063 inch (15 cm by 15 cm by 1.6 mm) 7075 T6 test panel previously chromic acid anodized and sealed as specified in Paragraph 11.E.(4) (other anodized panels may be used in 7000 series alloy).
使用标称尺寸为 6 英寸 x 6 英寸 x 0.063 英寸(15 厘米 x 15 厘米 x 1.6 毫米)的 7075 T6 测试板,之前已按第 11.E.(4)段规定进行铬酸阳极氧化处理和密封(可使用 7000 系列合金的其他阳极氧化板)。
2) Clean and mask. Scribe and remove mask to expose a nominal 1.5 inches by 1.5 inches (4 cm by 4 cm) square in center of panel.
清洁和遮蔽。划线并去除遮罩,在面板中心露出一个标称 1.5 英寸 x 1.5 英寸(4 厘米 x 4 厘米)的正方形。
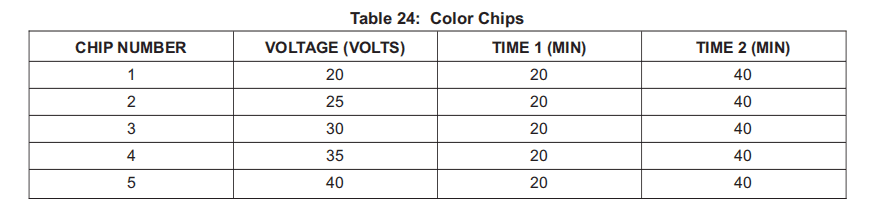
3) Strip nominal 1.5 inches by 1.5 inches (4 cm by 4 cm) square as specified in Paragraph 10.F.(4)(b) and anodize as specified in Paragraph 10.F.(4)(d) Make colored chips as shown in Table 24.
按照第 10.F.(4)(b)段的规定,剥去标称 1.5 英寸 x 1.5 英寸(4 厘米 x 4 厘米)的正方形,并按照第 10.F.(4)(d)段的规定进行阳极氧化处理,制成表 24 所示的彩色芯片。
4) Shear nominal 1.5 inches by 3.75 inches (4 cm by 10 cm) coupon from panel.
从面板上剪下标称 1.5 英寸 x 3.75 英寸(4 厘米 x 10 厘米)的试样。
5) Steel stamp voltage, time and date processed on each coupon. Color chips must be valid for up to 2 years from date processed or may be processed more frequently as deemed necessary.
在每个色片上盖上电压、时间和处理日期钢印。色片的有效期必须自处理之日起长达 2 年,也可视需要增加处理频率。
(d) Color Match Anodize Rework Process
配色阳极氧化返修工艺
1) Use electric heating blankets (Paragraph 7.B.(4)(b)4)) and a temperature controller (Paragraph 7.B.(4)(b)5)) to preheat area to be anodized. Maintain surface in the range of 92-98°F (33-37°C). Use thermocouple thermometer (Paragraph 7.B.(4)(b)2)) and surface probe (Paragraph 7.B.(4)(b)3)) to check temperature.
使用电热毯(第 7.B.(4)(b)4)和温度控制器(第 7.B.(4)(b)5)预热阳极氧化区域。保持表面温度在 33-37°C (92-98°F) 之间。使用热电偶温度计(第 7.B.(4)(b)2)和表面探针(第 7.B.(4)(b)3)检查温度。
2) Preheat anodize solution to 101-105°F (38-41°C), using a constant temperature bath (Paragraph 7.B.(4)(b)1)). Use only solution made up as specified in Paragraph 11.E.(7). Vendor procured solutions are not suitable.
使用恒温槽(第 7.B.(4)(b)1)将阳极氧化溶液预热至 101-105°F (38-41°C)。只能使用按第 11.E.(7)段规定配制的溶液。供应商提供的溶液不适用。
3) Use color chips (Paragraph 7.B.(4)(b)6)) to select voltage and time for anodizing in the range of 20-40 volts, and 20-40 minutes.
使用色片(第 7.B.(4)(b)6)段)选择阳极氧化的电压和时间,电压范围为 20-40 伏,时间范围为 20-40 分钟。
NOTE: Varying applied voltage and process time affects color as follows:
注: 不同的电压和处理时间对颜色的影响如下:
a) 20 volts gives a light color.
20 伏可获得浅色。
b) 40 volts gives a dark color.
40 伏可获得深色。
c) Intermediate voltages give a progressively darker color as voltage is increased above 20 volts.
当电压超过 20 伏时,中间电压的颜色会逐渐变深。
d) At a given voltage, the anodic color will also depend on the processing time. For window frames and forgings, use 40 minutes (marked on color chip). Leading edge slats are more difficult to judge because some of them have a thin anodize coating. Leading edge chips are made up in two different series, 20 minute anodize and 40 minute anodize. Select color chips which matches structure, and use whichever process time is marked on color chip.
在给定电压下,阳极颜色也取决于加工时间。对于窗框和锻件,使用 40 分钟(标在色片上)。前缘缝翼较难判断,因为有些有一层较薄的阳极氧化涂层。前缘色片分为 20 分钟阳极氧化和 40 分钟阳极氧化两个系列。选择与结构相匹配的色片,并使用色片上标明的工艺时间。
4) Select cathode size sufficient to cover defect area. Include excess to overlap mask.
选择足以覆盖缺陷区域的阴极尺寸。包括多余部分,以覆盖遮蔽。
5) Ramp-up voltage is selected value at rate of 10 V/min.
上升电压为选定值,速率为 10 V/分钟。
6) Anodize for preselected time.
阳极氧化预选时间。
7) Use slow back and forth motion of cathode to ensure even distribution of coating. Lift cathode from time to time to observe emerging color.
缓慢来回移动阴极,确保涂层均匀分布。不时抬起阴极,观察新出现的颜色。
NOTE: Color can be adjusted during the anodizing process. Check color against previously selected color chip as follows when approximately 1/2 of the selected process time has elapsed:
注: 颜色可在阳极氧化过程中调整。在所选工艺时间大约过了 1/2 时,按以下方法对照先前选择的色片检查颜色:
a) If color seems too light, raise voltage and color will get darker.
如果颜色太浅,提高电压,颜色会变深。
b) If color seems too dark, lower voltage and color will get lighter.
如果颜色太深,降低电压,颜色会变浅。
c) How much to change voltage takes some operator judgement based on experience. As a guide, increase or decrease voltage by 20 percent of set value.
改变电压的程度需要操作员根据经验来判断。作为指导,电压可按设定值的 20% 增减。
8) Keep the cathode and rework area wet with anodizing solution by using the preheated squeeze bottle to dispense solution periodically.
使用预热的挤压瓶定期注入阳极氧化溶液,以保持阴极和返工区湿润。
9) When anodizing time is completed, water rinse area.
阳极氧化结束后,用水冲洗该区域。
10) While area is wet, apply Henkel Corp Bonderite M-CR 1001 Aero solution (Paragraph 11.E.(2)). Maintain 2-3 minute contact time.
在该区域潮湿时,涂抹 Henkel Corp Bonderite M-CR 1001 Aero 溶液(第 11.E.(2)段)。保持 2-3 分钟的接触时间。
11) Rinse and dry the surface.
冲洗并擦干表面。
12) Remove mask.
取下遮蔽物。
11. PREPARATION OF SOLUTIONS 溶液的配制
A. References
参考文献

B. Maintenance Control
维护控制
(1) Make up and store the solutions in bottles (Paragraph 4.A.(3)(a)) that are clearly labeled with the solution name, the preparation date, and the total amp-hours/L used.
配制溶液并储存在瓶子里(第 4.A.(3)(a)段),瓶子上清楚地标明溶液名称、配制日期和所用总安培小时/升。
(2) Ensure tanks are clean before starting. Unless otherwise specified, prepare the processing solutions by performing the operations in the order listed. Mix the solutions thoroughly after each addition. Ensure that any added solid material has dissolved before adding another material.
开始前确保槽清洁。除非另有规定,否则应按所列顺序进行操作,配制处理溶液。每次加入溶液后都要充分混合。在添加另一种材料之前,应确保所添加的固体材料已经溶解。
(3) Water must meet the requirements of Paragraph 7.B.(6).
水必须符合第 7.B.(6)段的要求。
C. Chromate Conversion Solutions
铬酸盐转化溶液
(1) Sodium Dichromate-Sulfuric Acid
重铬酸钠-硫酸
(a) Make up sodium dichromate-sulfuric acid solution as follows for 1 liter:
1 升重铬酸钠-硫酸溶液的配制方法如下:
1) Place 0.6-0.7 liter of water in the container.
在容器中加入 0.6-0.7 升水。
2) Add 195-200 grams of sodium dichromate (Paragraph 3.H.(11)).
加入 195-200 克重铬酸钠(第 3.H.(11)段)。
3) Dissolve 0.16-0.18 grams of Stepan Nacconol 90G (Paragraph 3.H.(13)) in 45-55 mL of hot water and add to the solution.
在 45-55 毫升热水中溶解 0.16-0.18 克 Stepan Nacconol 90G(第 3.H.(13)段),并加入溶液中。
4) Slowly add 18.5-19.5 mL of sulfuric acid (Paragraph 3.H.(14)).
缓慢加入 18.5-19.5 毫升硫酸(第 3.H.(14)段)。
5) Add water to provide the desired final volume.
加水至所需的最终体积。
(b) Maintain the solution within the limits as shown in Table 25.
将溶液保持在表 25 所示的限度内。
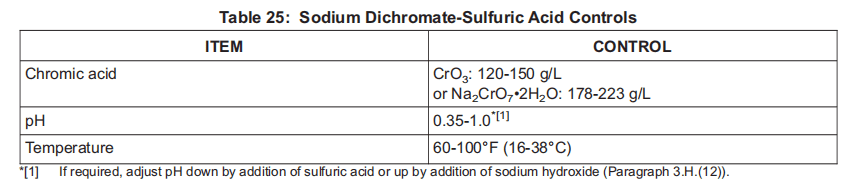
(2) MacDermid Iridite 80
(a) Make up MacDermid Iridite 80 solution as follows for 1 liter:
1 升 MacDermid Iridite 80 溶液的配制如下:
1) Place 0.6-0.7 liter of water in the container.
在容器中加入 0.6-0.7 升水。
2) Add 13-30 mL MacDermid Iridite 80 (Paragraph 3.G.(5)); (for acid zinc use 5-15 mL).
加入 13-30 mL MacDermid Iridite 80(第 3.G.(5)段);(酸性锌用 5-15 mL)。
3) Add water to the final volume.
加水至最终体积。
(b) Maintain the solution within the limits as shown in Table 26.
将溶液保持在表 26 所示的限度内。
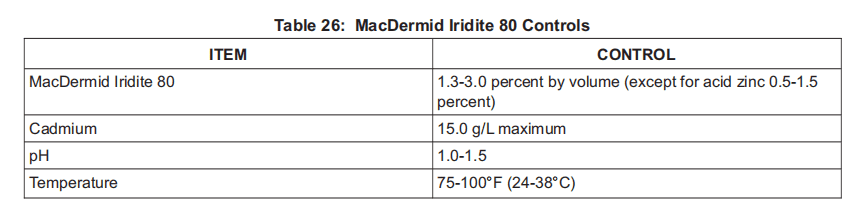
(3) MacDermid Iridite 8P
(a) Make up MacDermid Iridite 8P solution as follows for 1 liter:
1 升 MacDermid Iridite 8P 溶液的配制如下:
1) Place 0.6-0.7 liter of water in the container.
在容器中加入 0.6-0.7 升水。
2) Add 3.1-3.2 mL nitric acid (Paragraph 3.H.(6)).
加入 3.1-3.2 毫升硝酸(第 3.H.(6)段)。
3) Heat solution to 85-95°F (29-35°C).
将溶液加热至 85-95°F (29-35°C)。
4) Add 6-9 grams MacDermid Iridite 8P (Paragraph 3.G.(6)) and stir until dissolved.
加入 6-9 克 MacDermid Iridite 8P(第 3.G.(6)段)并搅拌至溶解。
5) Add water to the final volume.
加水至最终体积。
(b) Maintain the solution within the limits as shown in Table 27.
将溶液保持在表 27 所示的限度内。

D. Multiple Anodize Electrolyte Solution (MAE)
多重阳极氧化电解液 (MAE)
(1) Make up Multiple Anodize Electrolyte Solution as follows for 1 liter:
配制 1 升多重阳极氧化电解液的步骤如下:
(a) Place 0.5-0.6 liter of water in the container.
在容器中加入 0.5-0.6 升水。
(b) Slowly add 105-110 mL of sulfuric acid. Allow to cool to below 100°F (38°C) before proceeding.
缓慢加入 105-110 毫升硫酸。冷却至低于 38°C (100°F) 后再继续。
(c) In a separate container, mix 10.0-10.5 mL of glycerin (Paragraph 3.H.(3)) and 14.5-15.0 mL of glycolic acid (Paragraph 3.H.(4)). Add this solution to the acid solution.
在另一个容器中,混合 10.0-10.5 毫升甘油(第 3.H.(3)段)和 14.5-15.0 毫升乙醇酸(第 3.H.(4)段)。将此溶液加入酸溶液中。
(d) Add water to the desired final volume.
加水至所需的最终体积。
(2) Maintain the solution within the limits as shown in Table 28.
将溶液保持在表 28 所示的限度内。

E. Anodize Seal Solutions
阳极氧化密封溶液
(1) Henkel Corp Bonderite M-CR 600 Aero Solution
(a) Make up Henkel Corp Bonderite M-CR 600 Aero Solution as follows for 1 liter:
按以下方法配制 1 升 Henkel Corp Bonderite M-CR 600 Aero 溶液:
1) Place 0.6-0.7 liter of water in the container.
在容器中加入 0.6-0.7 升水。
2) Add 14.5-15.5 grams of Henkel Corp Bonderite M-CR 600 Aero (Paragraph 11.E.(1)).
加入 14.5-15.5 克 Henkel Corp Bonderite M-CR 600 Aero(第 11.E.(1)段)。
3) Add water to the desired final volume.
加水至所需的最终体积。
(b) Maintain the solution within the limits as shown in Table 29.
将溶液保持在表 29 所示的限度内。

(2) Henkel Corp Bonderite M-CR 1001 Aero Solution
(a) Make up Henkel Corp Bonderite M-CR 1001 Solution as follows for 1 liter:
按以下方法配制 1 升 Henkel Corp Bonderite M-CR 1001 溶液:
1) Place 0.4-0.5 liter of water in the container.
在容器中加入 0.4-0.5 升水。
2) Add 380-420 mL of Henkel Corp Bonderite M-CR 1001 Aero Liquid (Paragraph 11.E.(2)).
加入 380-420 毫升 Henkel Corp Bonderite M-CR 1001 Aero 液体(第 11.E.(2)段)。
3) Add water to the desired final volume.
加水至所需的最终体积。
(b) Maintain the solution within the limits as shown in Table 30.
将溶液保持在表 30 所示的限度内。
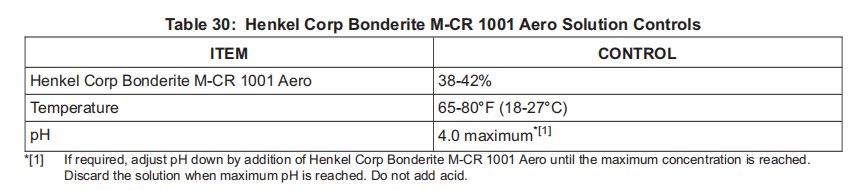
(3) Dilute Chromate Seal Solution
稀铬酸盐密封溶液
(a) Make up Dilute Chromate Seal Solution as follows for 100 liters:
100 升稀释铬酸盐密封溶液的配制方法如下:
1) Add 50-80 L of deionized water to the container.
在容器中加入 50-80 升去离子水。
2) Add 6.5-7.2 g chromium trioxide (Paragraph 3.H.(2)).
加入 6.5-7.2 克三氧化二铬(第 3.H.(2)段)。
3) Add one of the following:
加入以下其中一种:
a) 6.5-7.2 g magnesium chromate (Paragraph 3.H.(5)).
6.5-7.2 克铬酸镁(第 3.H.(5)段)。
b) 5.5-6.1 g potassium chromate (Paragraph 3.H.(8)).
5.5-6.1 克铬酸钾(第 3.H.(8)段)。
c) 4.5-5.0 g sodium chromate (Paragraph 3.H.(10)).
4.5-5.0 克铬酸钠(第 3.H.(10)段)。
4) Add deionized water to the desired final volume.
加入去离子水至所需的最终体积。
(b) Maintain the solution within the limits as shown in Table 31.
保持溶液在表 31 所示的限度内。
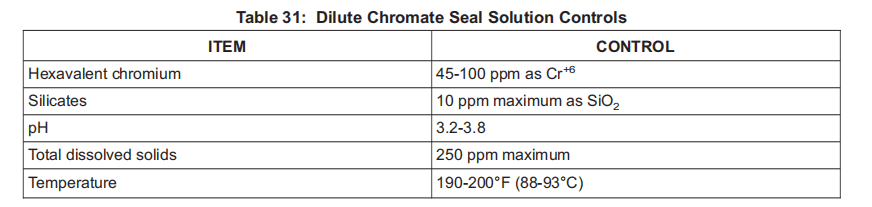
(c) Maintain hexavalent chromium concentration by adding chromium trioxide, sodium chromate, potassium chromate, or magnesium chromate.
加入三氧化二铬、铬酸钠、铬酸钾或铬酸镁,以保持六价铬浓度。
(d) Maintain pH by adding sodium hydroxide.
加入氢氧化钠以保持 pH 值。
(e) Discard or purify the solution when silicates or total dissolved solids reach the upper limits.
当硅酸盐或总溶解固体达到上限时,报废或净化溶液。
(f) Use deionized water for solution replenishment.
使用去离子水补充溶液。
(g) Maintain the solution free of visible sediment.
保持溶液无可见沉淀物。
(4) Deionized Water Seal – Control
去离子水密封 – 控制
(a) Deionized Water Seal limits as shown in Table 32.
去离子水封的限度如表 32 所示。
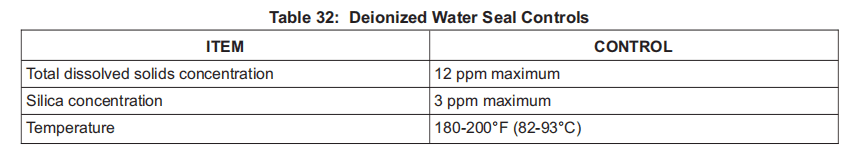
(5) Silver Plating Solution
电镀银溶液
(a) This solution is an alternative to LDC-4701 Silver Hi-Build (Paragraph 3.B.(7)(a)) and Sifco Process Silver (Hard Heavy Build), 3083 (Paragraph 3.B.(7)(c)).
本溶液是 LDC-4701 Silver Hi-Build (第 3.B.(7)(a)段)和 Sifco Process Silver (Hard Heavy Build), 3083 (第 3.B.(7)(c)段)的替代品。
(b) Make up Silver Plating Solution as follows for 1 liter:
1 升电镀银溶液的配制方法如下:
1) Place 0.6-0.7 liter of water in the container.
在容器中加入 0.6-0.7 升水。
2) Add 41-45 grams of potassium carbonate (Paragraph 3.H.(7)).
加入 41-45 克碳酸钾(第 3.H.(7)段)。
3) Add 23-25 grams of potassium cyanide (Paragraph 3.H.(9)).
加入 23-25 克氰化钾(第 3.H.(9)段)。
4) Add 17.5-18.5 grams of silver cyanide (Reference Not Currently Available).
加入 17.5-18.5 克氰化银(参考资料暂缺)。
5) Add water to the desired final volume.
加水至所需的最终体积。
(c) Maintain the solution within the limits as shown in Table 19.
将溶液保持在表 19 所示的限度内。
(d) Discard the solution after one use.
溶液使用一次后报废。
(6) Nickel and Nickel-Tungsten Stripping Solution
镍和镍钨剥离溶液
(a) Make up Nickel-Tungsten Stripping Solution as follows for 1 liter:
1 升镍钨剥离液的配制方法如下:
1) Place 0.44-0.46 liter of room temperature (or cooler) water in the container and place the container in an ice bath.
在容器中加入 0.44-0.46 升室温(或更低温)水,并将容器放入冰浴中。
2) Slowly add 0.49-0.51 liter of sulfuric acid in increments.
缓慢加入 0.49-0.51 升硫酸。
a) Allow the solution to cool between additions.
在两次添加之间让溶液冷却。
3) Add 49-51 mL of glycerin.
加入 49-51 毫升甘油。
4) Add water, if needed, to the desired final volume.
必要时加水至所需的最终体积。
(b) Use at 60-120°F (16-49°C) and discard after one use.
在 60-120°F (16-49°C) 温度下使用,使用一次后报废。
(7) Chromic Acid Anodize Solution
铬酸阳极氧化溶液
(a) Make up Chromic Acid Anodize Solution as specified in SOPM 20-43-01 and as follows:
按照 SOPM 20-43-01 的规定和以下步骤配制铬酸阳极氧化溶液:
1) A nominal concentration of 40 g/L chromium trioxide (CrO3 ) in water.
标称浓度为 40 克/升的三氧化二铬(CrO3)水溶液。
(8) Boric Acid-Sulfuric Acid Anodizing Solution (BSAA)
硼酸-硫酸阳极氧化溶液(BSAA)
(a) Make up BSAA as follows for 1 liter:
1 升硼酸-硫酸阳极氧化溶液的配制方法如下:
1) Place 0.7-0.8 L of water in the container.
在容器中加入 0.7-0.8 升水。
2) Add 40-45 g sulfuric acid.
加入 40-45 克硫酸。
3) Add 7-8 g boric acid (Paragraph 3.H.(1)).
加入 7-8 克硼酸(第 3.H.(1)段)。
4) Add water to the desired final volume.
加水至所需的最终体积。
(b) Maintain the solution within the limits as shown in Table 33.
保持溶液在表 33 所示的限度内。
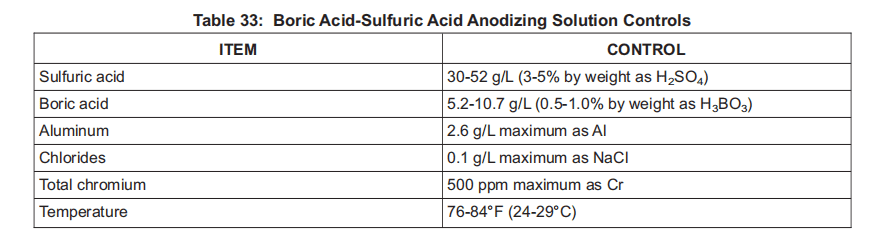
(c) Maintain the solution by adding sulfuric acid and boric acid or by removing solution and adding water, sulfuric acid and boric acid.
通过加入硫酸和硼酸或通过去除溶液并加入水、硫酸和硼酸来保持溶液。
12. QUALITY CONTROL 质量控制
A. Assure that the requirements of this specification are met by monitoring the process and examining the end-items in accordance with established quality assurance provisions.
根据既定的质量保证规定,通过监控过程和检查最终产品,确保满足本规范的要求。
(1) Verify that only currently certified and appropriately maintained equipment (Paragraph 7.) is used for performing this process.
确认只有经过认证和适当维护的设备(第 7.段)才可用于执行此工序。
(2) Areas of brush plating or anodizing and electrical ground contact areas must be visually examined for arc burns.
必须目视检查电镀或阳极氧化区域和电气接地接触区域是否有电弧烧伤。
(3) Brush plating and anodizing must meet the requirements of the coatings in accordance with Paragraph 13.B.
电镀和阳极氧化必须符合第 13.B 段规定的涂层要求。
(4) Inspect parts for color match when the part is reworked in accordance with Paragraph 10.F.(4)(d).
按照第 10.F.(4)(d)段的规定,在重新加工零件时检查零件的颜色是否匹配。
(5) Compressed air must be tested with sufficient sampling and frequency to assure compliance with the requirement in Paragraph 7.
压缩空气必须以足够的取样和频率进行测试,以确保符合第 7 段的要求。
(6) Tanks for solutions which require temperature control must be tested at intervals as necessary to assure the temperature requirements of this specification are met.
需要温度控制的溶液槽必须按必要的时间间隔进行测试,以确保符合本规格的温度要求。
13. REQUIREMENTS 要求
A. References
参考资料
B. Plating and Anodizing Requirements
电镀和阳极氧化要求
(1) Electrolytically formed coatings applied in accordance with this specification must fulfill the appearance, adhesion, and acceptance criteria of the applicable specifications identified in Table 34.
按照本规范使用的电解成型涂层必须符合表 34 中所列适用规范的外观、附着力和验收标准。
(2) Adhesion is verified by operator certification and demonstration of proficiency along with process surveillance or by an adhesion test in accordance with BSS7235.
附着力通过操作员认证和熟练程度证明以及过程监控或通过符合 BSS7235 的附着力测试来验证。